Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3443-3456
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3443
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3443
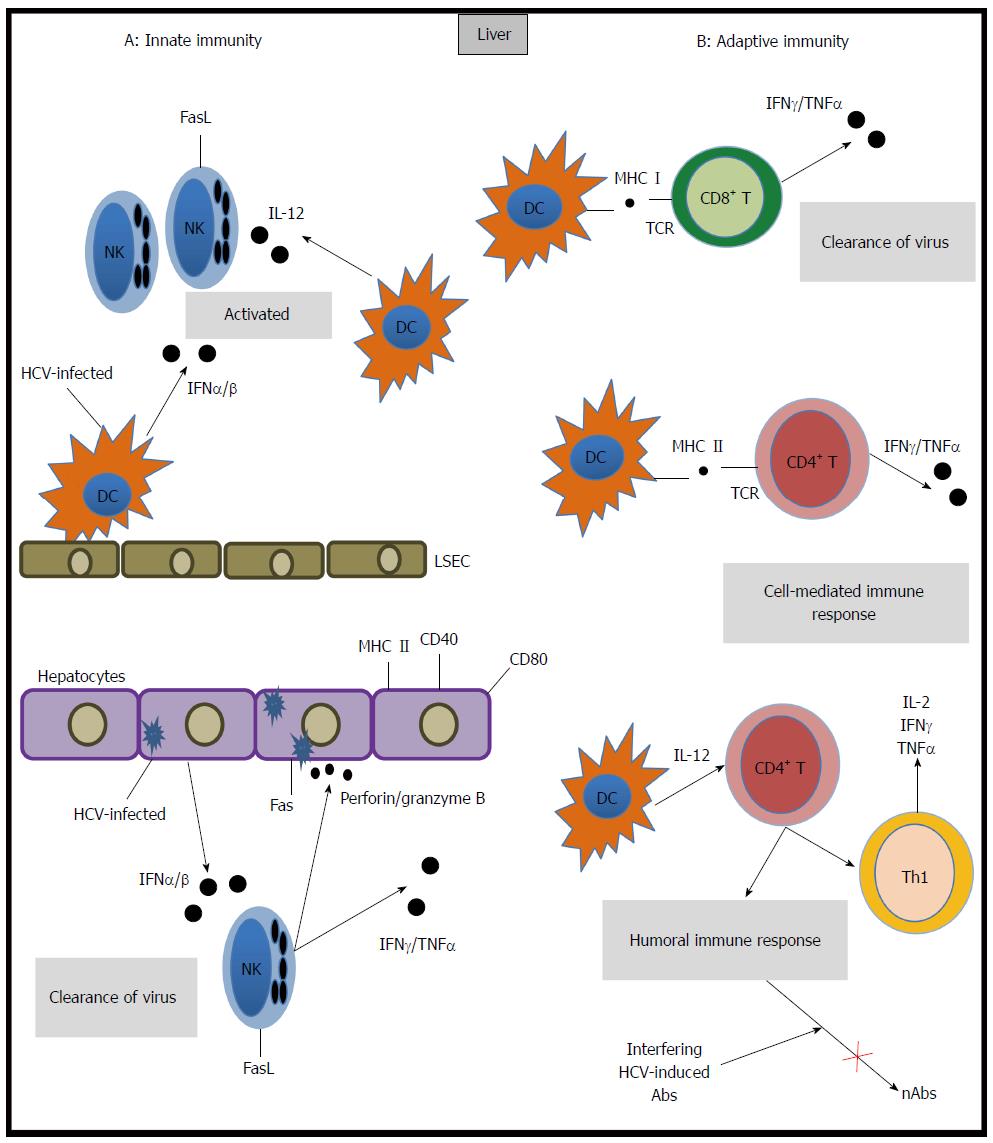
Figure 1 Mechanisms of Immune response to hepatitis C virus.
Multiple innate (A) and adaptive immune (B) components are involved in hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (see text), dendritic cells (DC), natural killer (NK) cells, CD4+, CD8+ T cells and B-cell mediated humoral immune response are crucial for disease outcome. IFN-γ: interferon-gamma; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: Interleukin; nAbs: Neutralizing anti-HCV antibodies.
- Citation: Fierro NA, Gonzalez-Aldaco K, Torres-Valadez R, Martinez-Lopez E, Roman S, Panduro A. Immunologic, metabolic and genetic factors in hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3443-3456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3443.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3443