Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3418-3430
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418
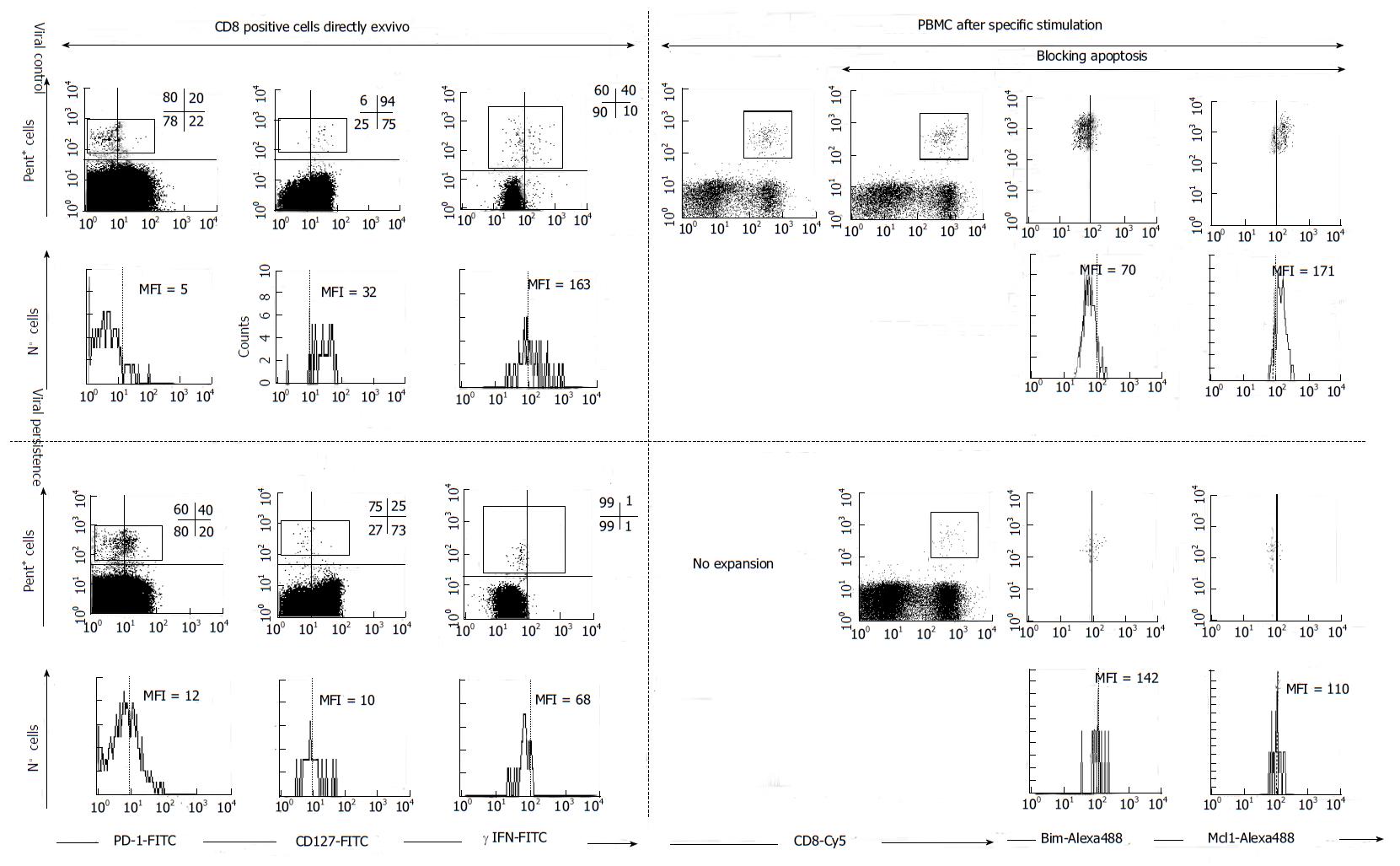
Figure 4 FACS® dot-plots and histograms of hepatitis C virus-specific CD8+ cells from hepatitis C virus patients with different viral control.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV)-specific CD8+ cells were stained with Abs anti γ-IFN, anti-PD-1, anti-CD127, anti-Mcl-1, anti-Bim, anti-CD8 plus pentameric HLA-A2/NS31406 peptide complexes. PD1, γ-IFN and CD127 was analyzed directly ex vivo. Antigen specific proliferation was assessed after blocking or not apoptosis. After expansion Bim and Mcl-1 expression was analyzed. HCV-specific CTLs controlling HCV infection expressed a CD127high, PD-1low, Mcl-1high and Bimlow phenotype while CTLs not controlling HCV displayed the opposite phenotype. MFI: mean fluorescence intensity, Pent: Pe-HLA-A2/NS31406 pentameric complexes. PBMC: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells. PD-1: Programmed cell death protein 1; IFN: Interferon; Bim: Bcl-2-interacting mediator; Mcl-1: Myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein.
- Citation: Larrubia JR, Moreno-Cubero E, Lokhande MU, García-Garzón S, Lázaro A, Miquel J, Perna C, Sanz-de-Villalobos E. Adaptive immune response during hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3418-3430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418