Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3418-3430
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418
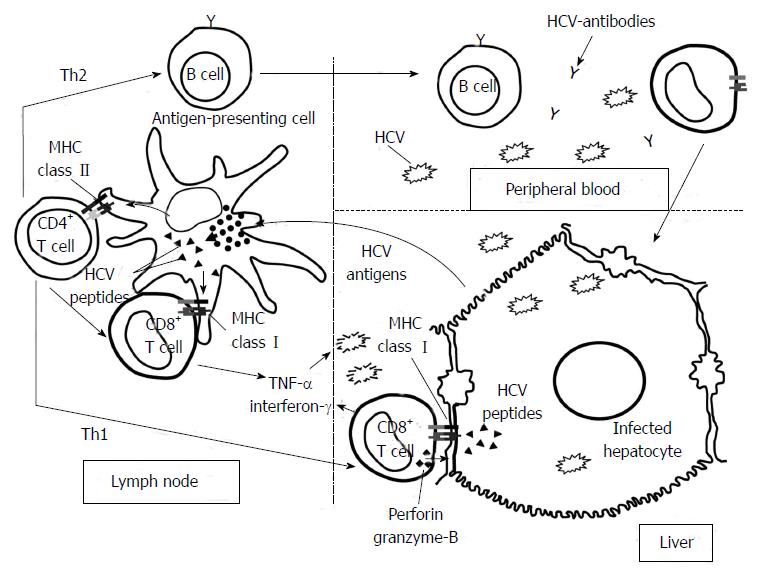
Figure 1 Hepatitis C virus-specific immune response activation.
Graph showing the priming of naïve T cells by professional antigen-presenting cells in the lymph nodes after antigen up-take in the liver. After specific-T cell activation, these cells become effector T helper (Th) and cytotoxic T cells (CTL) and they migrate into the liver. Th2 response regulates B cells while Th1 response controls CTLs effector function. Specifc-CTLs are able to destroy hepatitis C virus (HCV) by cytolytic and non-cytolytic mechanisms.
- Citation: Larrubia JR, Moreno-Cubero E, Lokhande MU, García-Garzón S, Lázaro A, Miquel J, Perna C, Sanz-de-Villalobos E. Adaptive immune response during hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3418-3430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3418