Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2014; 20(12): 3301-3311
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3301
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3301
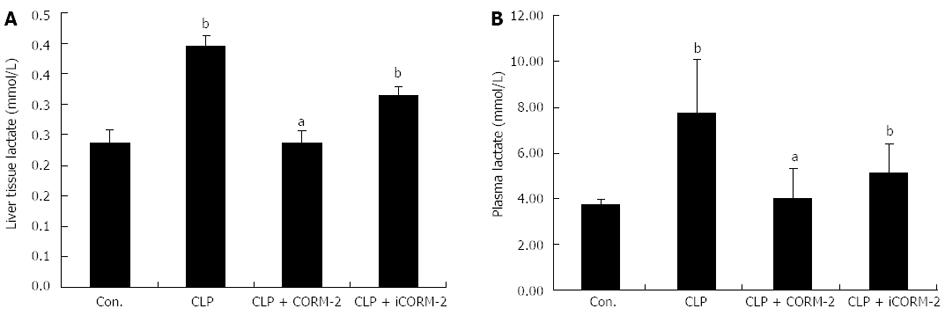
Figure 8 Effect of carbon monoxide-releasing molecule II on hepatic lactate production in septic mice.
Mice were challenged with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) and treated with tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer (CORM-2) or iCORM-2 as described in the Methods section. Lactate production in hepatic homogenates (A) and plasma (B) were assessed 24 h after CLP injury. When compared with the sham group, the CLP groups had significantly higher levels of lactic acid. After CORM-2 intervention, lactic acid levels in plasma and hepatic homogenates declined significantly. Results are presented as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs sham mice; aP < 0.05 vs CLP mice.
- Citation: Liang F, Cao J, Qin WT, Wang X, Qiu XF, Sun BW. Regulatory effect and mechanisms of carbon monoxide-releasing molecule II on hepatic energy metabolism in septic mice. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(12): 3301-3311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i12/3301.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3301