Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2014; 20(12): 3301-3311
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3301
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3301
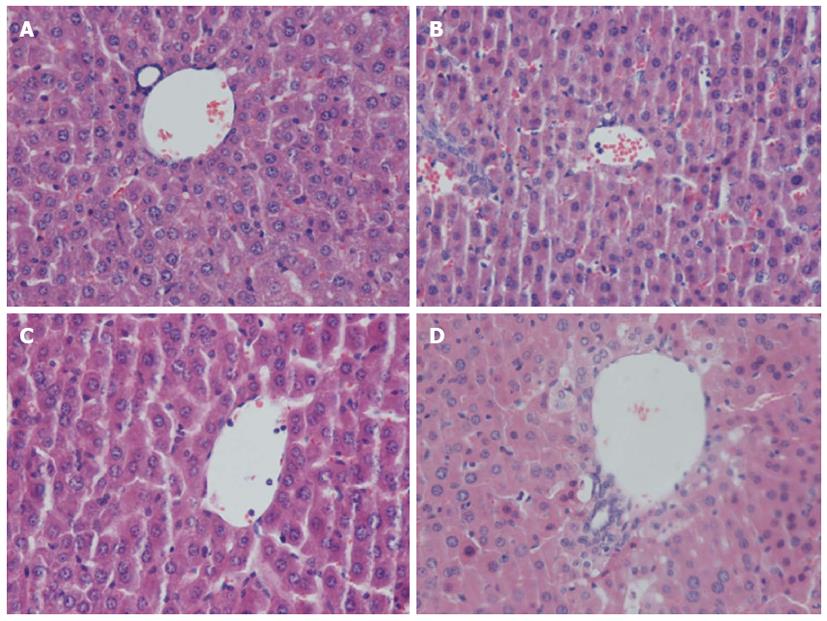
Figure 3 Effect of carbon monoxide-releasing molecule II on liver injury in septic mice.
Mice were challenged with cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) and treated with tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) dimer (CORM-2) or iCORM-2 as described in the Methods section. Morphologic characteristics at 24 h after CLP were observed under light microscopy with hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Liver specimens from mice in the CLP group showed sinusoidal dilatation and congestion, hepatocellular swelling, vacuolar changes in partial hepatocytes, and neutrophil infiltration. However, in the CLP + CORM-2 group, hepatocellular damage was obviously less severe and the extent of hepatic neutrophil infiltration was reduced. A: Sham; B: CLP; C: CLP + CORM-2; D: CLP + iCORM-2.
- Citation: Liang F, Cao J, Qin WT, Wang X, Qiu XF, Sun BW. Regulatory effect and mechanisms of carbon monoxide-releasing molecule II on hepatic energy metabolism in septic mice. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(12): 3301-3311
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i12/3301.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3301