Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2014; 20(12): 3223-3230
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3223
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3223
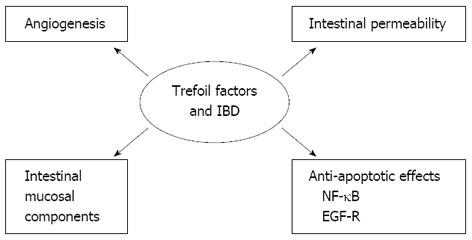
Figure 1 Role of trefoil factors in inflammatory bowel disease.
The potential mechanisms involving anti-apoptotic properties, migration and invasion, angiogenesis, and interaction with mucins. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; EGF-R: Epidermal growth factor receptor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B.
- Citation: Aamann L, Vestergaard EM, Grønbæk H. Trefoil factors in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(12): 3223-3230
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i12/3223.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3223