Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2014; 20(12): 3100-3111
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3100
Published online Mar 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3100
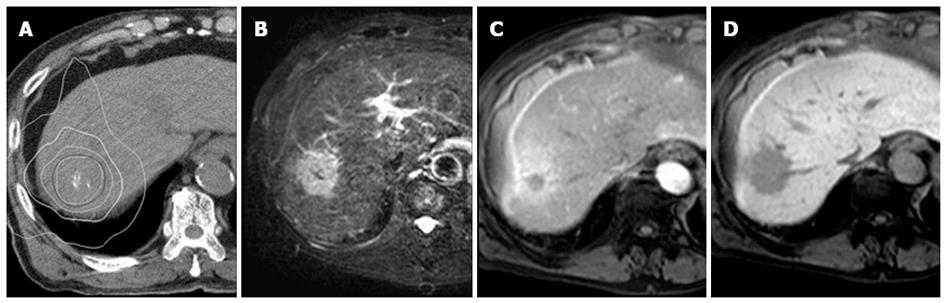
Figure 7 Typical focal liver reaction 4 mo after stereotactic body radiation therapy seen on gadoxetate acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
An axial view of radiation dose distribution (A). The isodose lines (white lines) from inner to outer represent 40, 30, 20, and 10 Gy, respectively. A T2-weighted image shows a high-intensity area corresponding to a high-dose area (B), which is seen as an enhanced area in early phase after injection of gadoxetate acid (C). The hepatobiliary phase shows a well-demarcated low-intensity area (D).
- Citation: Sanuki N, Takeda A, Kunieda E. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(12): 3100-3111
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i12/3100.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3100