Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2014; 20(11): 3050-3055
Published online Mar 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.3050
Published online Mar 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.3050
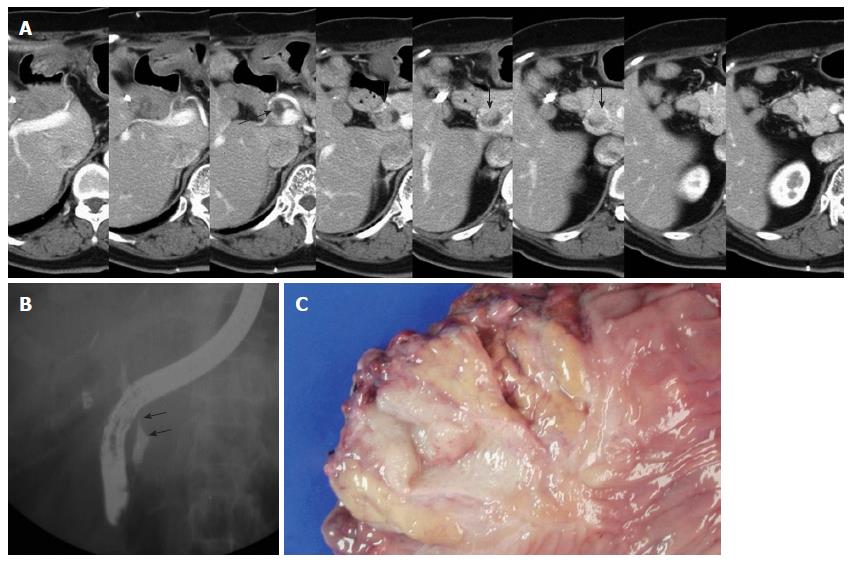
Figure 1 Imaging findings and gross specimen of the later metachronous bile duct tumor in case 1.
A: The arrow indicates the dilated remnant distal bile duct, and the arrow heads indicate the polypoid mass lesion of the distal remnant bile duct; B: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography revealed mild dilatation of the intrapancreatic remnant bile duct with a filling defect (arrows); C: A gross examination of the resected specimen shows a polypoid mass arising from the remnant bile duct with invasion into the pancreas.
-
Citation: Kwon HJ, Kim SG, Chun JM, Hwang YJ. Classifying extrahepatic bile duct metachronous carcinoma by
de novo neoplasia site. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(11): 3050-3055 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i11/3050.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.3050