Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2014; 20(10): 2653-2663
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2653
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2653
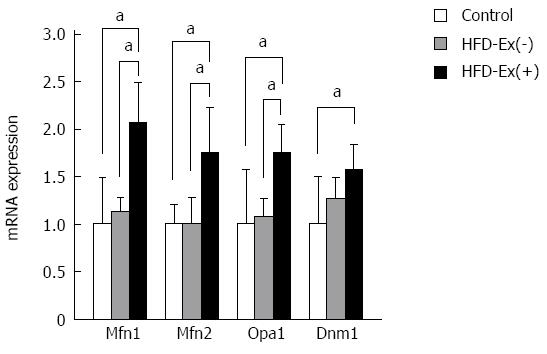
Figure 6 Effects of exenatide on the expression levels of mitochondrial morphologic regulators in adipose tissue.
Genes involved in mitochondrial fusion [mitofusin-1 (Mfn1) and mitofusin-2 (Mfn2) and optic atrophy-1 (Opa1)] were significantly greater in the high-fat diet (HFD)-Ex(+) group than in the control and HFD-Ex(-) groups. The expression of dynamin-1 (Dnm1), which is involved in mitochondrial fission, was not significantly different between the HFD-Ex(+) and HFD-Ex(-) groups. The fold changes were calculated as the ratio of the expression level in the HFD-Ex(+) or HFD-Ex(-) group to that in the control group. n = 8, aP < 0.05 between groups.
- Citation: Tanaka K, Masaki Y, Tanaka M, Miyazaki M, Enjoji M, Nakamuta M, Kato M, Nomura M, Inoguchi T, Kotoh K, Takayanagi R. Exenatide improves hepatic steatosis by enhancing lipid use in adipose tissue in nondiabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(10): 2653-2663
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i10/2653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2653