Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2014; 20(10): 2653-2663
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2653
Published online Mar 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2653
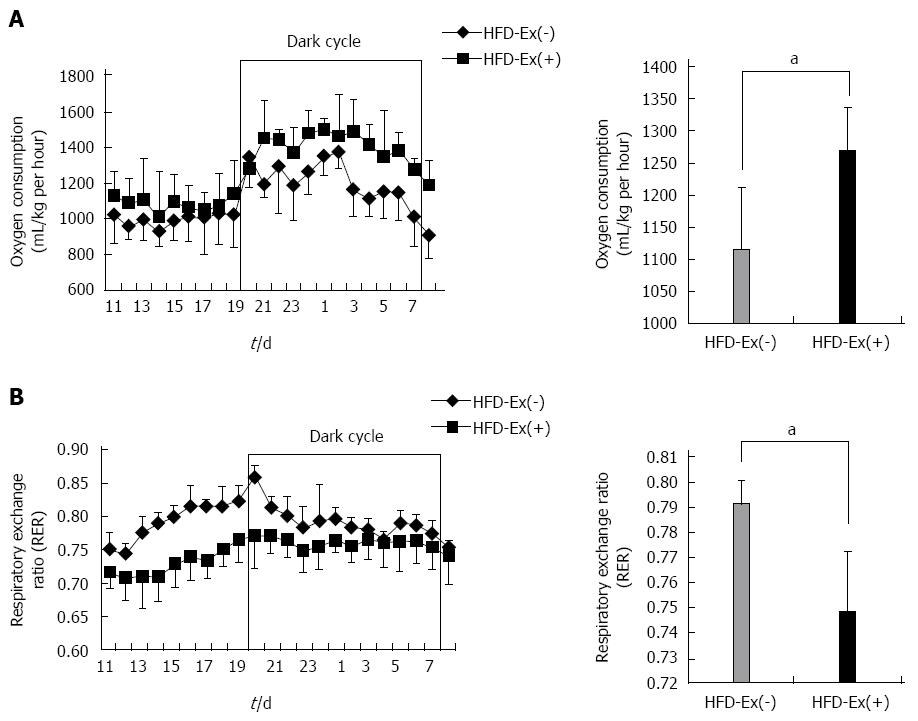
Figure 2 Oxygen consumption and respiratory exchange ratio evaluated by indirect calorimetry in the high-fat diet-Ex(+) and high-fat diet-Ex(-) groups at week 12 of feeding.
A: Oxygen consumption was significantly greater in the high-fat diet (HFD)-Ex(+) group than in the HFD-Ex(-) group, particularly during the dark cycle; B: Respiratory exchange ratio (RER) was significantly lower in the HFD-Ex(+) group than in the HFD-Ex(-) group. n = 4. aP < 0.05 between groups.
- Citation: Tanaka K, Masaki Y, Tanaka M, Miyazaki M, Enjoji M, Nakamuta M, Kato M, Nomura M, Inoguchi T, Kotoh K, Takayanagi R. Exenatide improves hepatic steatosis by enhancing lipid use in adipose tissue in nondiabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(10): 2653-2663
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i10/2653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i10.2653