Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 250-257
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.250
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.250
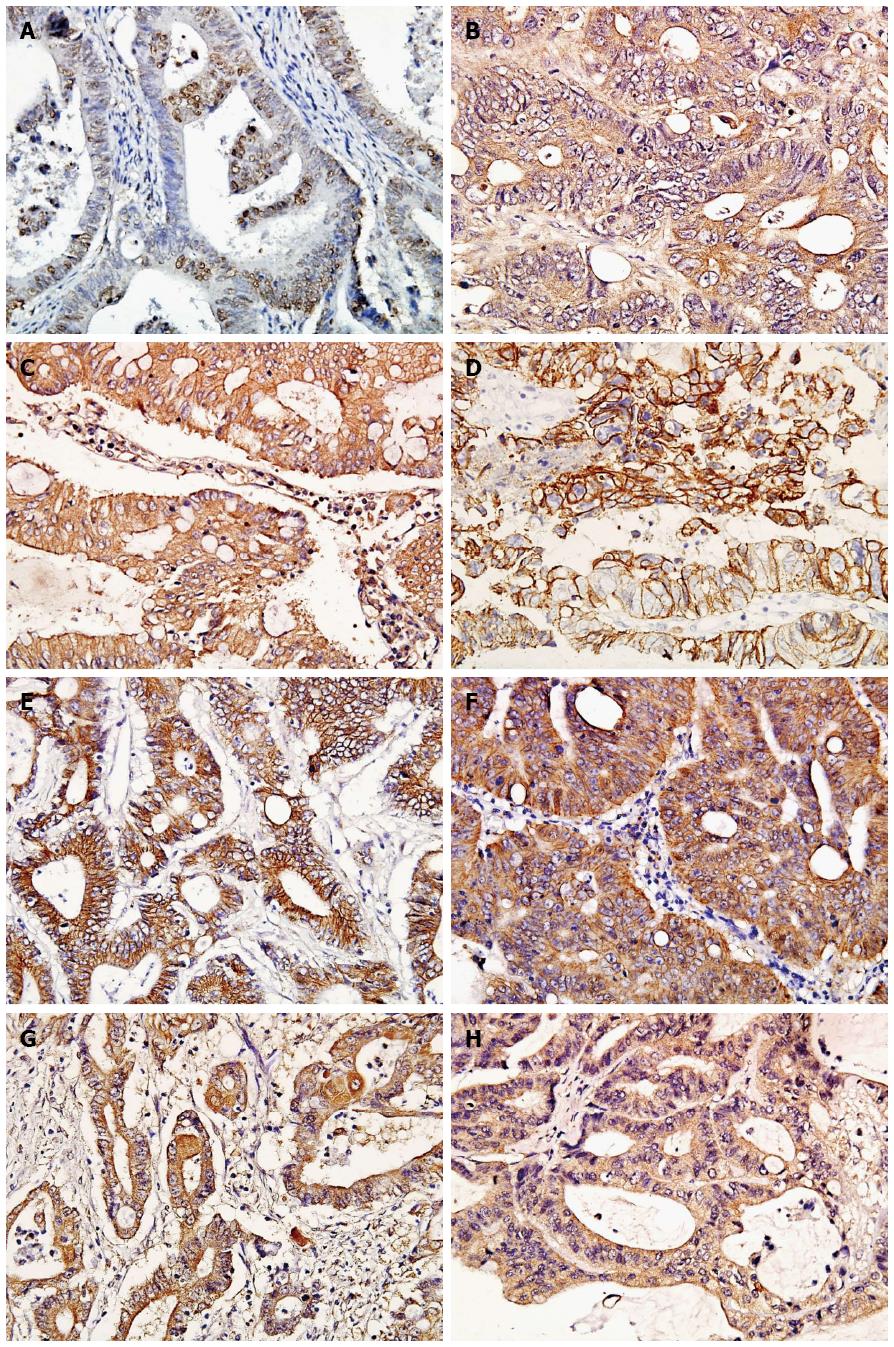
Figure 1 Immunophenotypes of the investigated antigens in Lynch syndrome (× 400 magnification).
A: hMSH2 (Positive staining located in the nucleolus); B: hMLH1 (Positive staining located in the cytoplasm); C: TGFβRII (Positive staining located in the cytomembrane and cytoplasm); D: E-cadherin (Positive staining located in the cytomembrane); E: Cytomembrane β-catenin (Positive staining located in the cytomembrane); F: Cytoplasmic β-catenin (Positive staining located in the cytoplasm); G: MMP-7 (Positive staining located in the cytoplasm); H: TIMP-2 (Positive staining located in the cytoplasm).
- Citation: Gu GL, Zhu XQ, Wei XM, Ren L, Li DC, Wang SL. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer tissue of patients with Lynch syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 250-257
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/250.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.250