Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 22-30
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
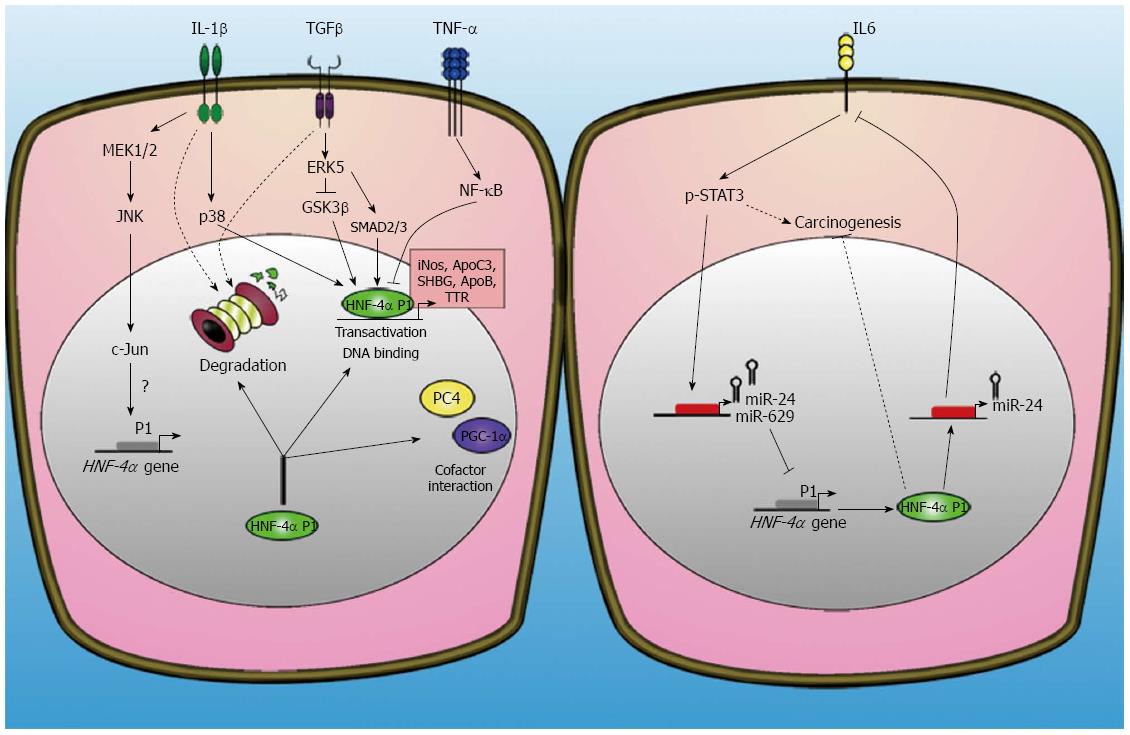
Figure 2 Cytokines effect on hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha activity and inflammation associated-cancer in hepatocytes.
Cytokines regulate hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4-α) function through its proteosomal degradation, DNA binding affinity, transcriptional activity and cofactor interaction (left panel). HNF4-α participates also to a retro-inhibition feedback loop of the oncogenic interleukin (IL)-6/STAT3 pathway (right panel). In hepatocytes, HNF4-α binds to miR-124 promoter and activates its transcription. MiR-124 targets IL-6 receptor transcript to decrease its expression and then block the activation of IL-6 pathway. On the other hand, stimulation of hepatocytes by IL-6 activates the phosphorylation of STAT3 that binds and transactivates the promoters of miR-24 and miR-629. These two microRNA target HNF4-α transcript and decrease its expression to relieve inhibition of the IL-6 pathway. The perturbation of this molecular circuit ultimately results in the sustained activation of the oncogenic STAT3 pathway and the loss of the tumour suppressor effect of HNF4-α P1 isoforms.
- Citation: Babeu JP, Boudreau F. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 22-30
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/22.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22