Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 22-30
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22
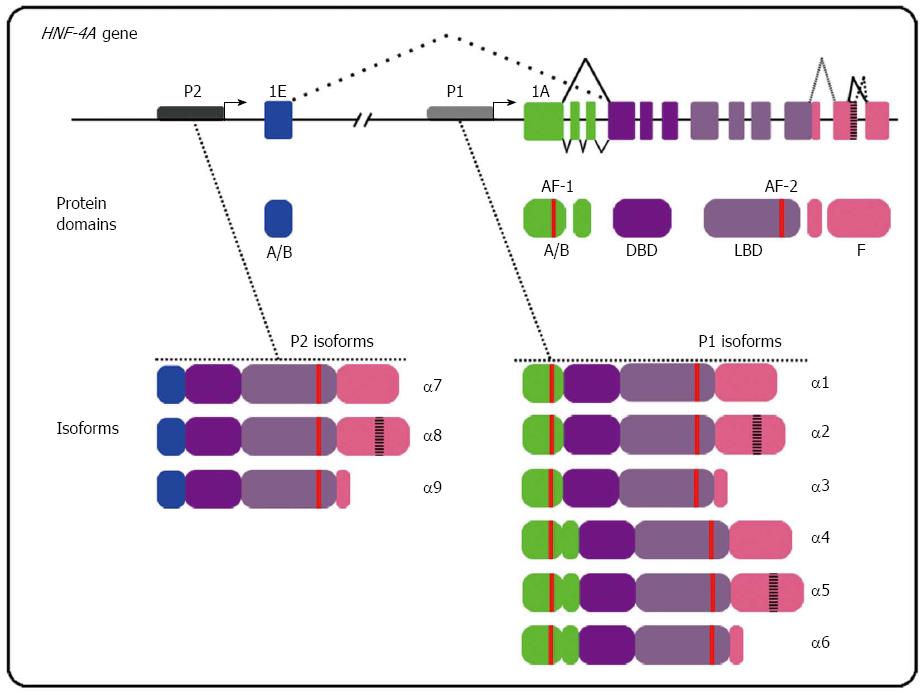
Figure 1 Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha P1 and P2 isoforms classes originate from alternative promoters and splicing.
HNF4-α contains two distinct promoters (P1 and P2) that drive expression of nine known isoforms (α1 to α9). Transcription through the P1 promoter allows the inclusion of the exon 1A coding for the N-terminal domain of HNF4-α. P1 isoforms class displays a N-terminal region containing the cofactor interacting domain designed as AF-1. Transcription through the P2 promoter allows the inclusion of the exon 1E but the exclusion of the exon 1A. P2 isoforms class displays a smaller N-terminal domain than P1 isoforms and does not contain the AF-1 region. Alternative splicing of the last exons of HNF4A modifies the regulating F domain of both isoforms classes while alternative splicing of exon 1A modifies only A/B domain of the P1 isoforms. HNF4-α: Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha; DBD: DNA binding domain; LBD: Ligand binding domain; AF-1: Activating function-1; AF-2: Activating function-2.
- Citation: Babeu JP, Boudreau F. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha involvement in liver and intestinal inflammatory networks. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 22-30
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/22.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.22