Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 193-203
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.193
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.193
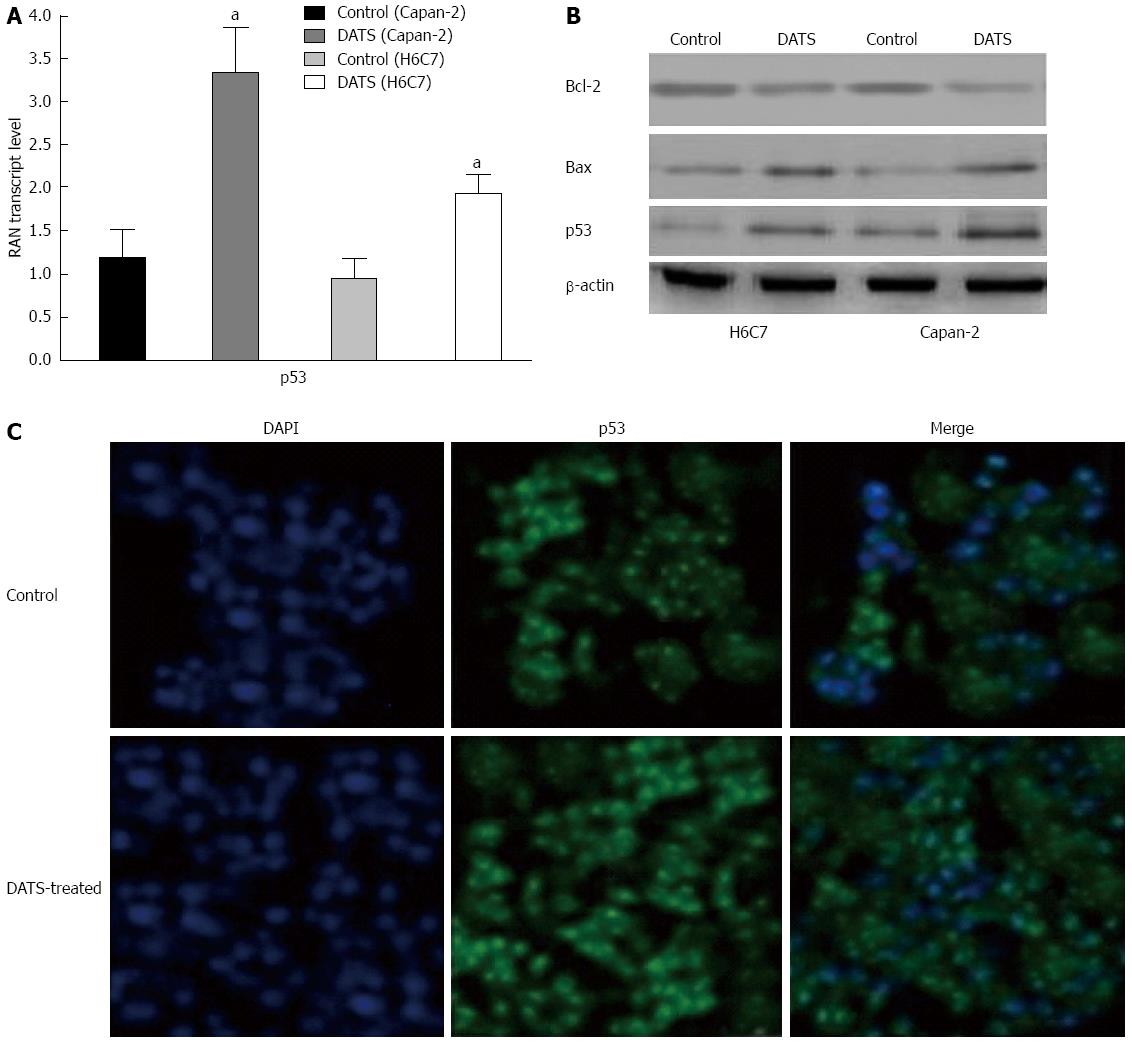
Figure 5 Diallyl trisulfide upregulates Bax expression and deregulates Bcl-2 expression and p53 translocation to the nucleus in Capan-2 cells.
A and B: Cells were treated with 100 μmol/L of diallyl trisulfide (DATS) for 24 h (aP < 0.05 vs control). Cells were lysed and total protein was collected and subjected to Western blot analysis to determine p53, Bax and Bcl-2 protein expression levels in treated and untreated control cells. β-actin was used as a loading control; C: The subcellular localization of p53 was indicated by the green FITC, while the position of the nucleus was shown by the blue DAPI staining. Individual images for p53 localization in the nucleus were taken at a magnification of × 400. Images were merged to display the subcellular localization of p53, using ECLIPSE. Representative data from three independent experiments are shown. DAPI: 4',6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Ma HB, Huang S, Yin XR, Zhang Y, Di ZL. Apoptotic pathway induced by diallyl trisulfide in pancreatic cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 193-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/193.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.193