Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 175-182
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.175
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.175
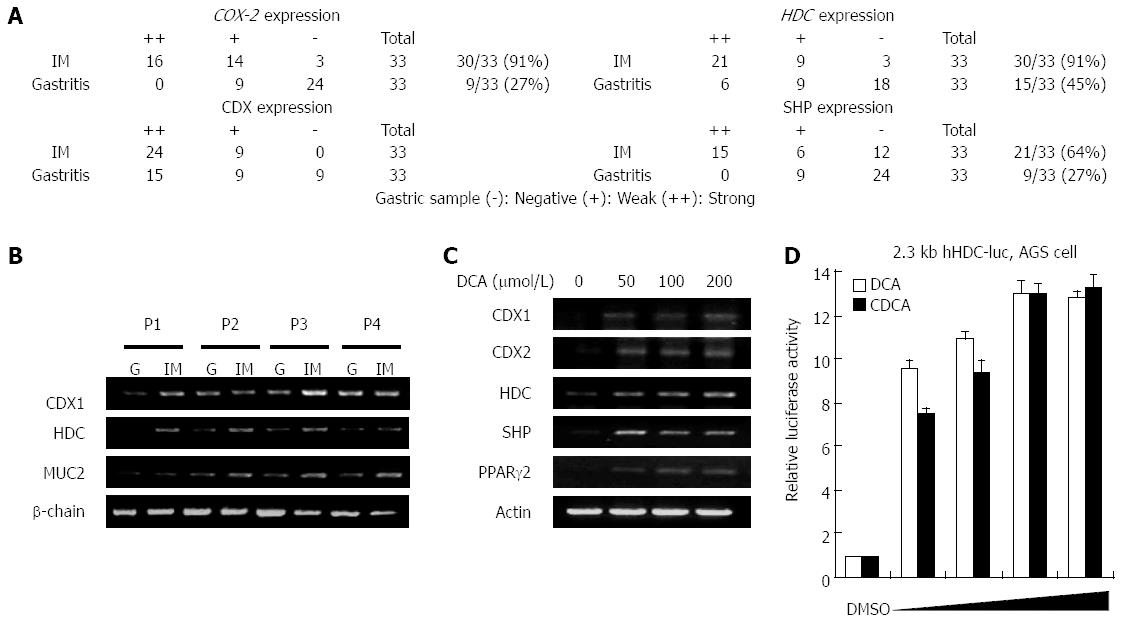
Figure 1 Relative expression levels of histidine decarboxylase in gastritis patients with or without intestinal metaplasia and bile acid-treated cells.
A: mRNA expression patterns of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2), caudal-related homeobox family (CDX1), small heterodimer partner (SHP), and histidine decarboxylase (HDC) in 11 patients. Tissue samples for molecular analysis were collected from patients undergoing gastritis surgery or endoscopy for diagnosis of gastric disease. Numbers represent patient numbers showing the same intensity of mRNA expression; B: Total RNA was prepared from four gastric mucosa samples representing gastritis and intestinal metaplasia, after which CDX1, HDC, and mucin (MUC)2 mRNA levels were measured by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) with β-actin as a loading control; C: MKN45 cells were maintained either under control conditions (DMSO) or in the presence of various concentrations of bile acids (deoxycholic acid, DCA) for 24 h. Total RNA was prepared from the cells, after which mRNA levels of CDX, HDC, SHP, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ2 were assessed by RT-PCR; D: Human gastric adenocarcinoma (AGS) cells were transfected with the 2.3 kb HDC-luc promoter construct and maintained either under control conditions (DMSO) or in the presence of various concentrations (10, 20, 50, and 100 μmol/L) of bile acids (DCA; chenodeoxycholic acid, CDCA) for 24 h. Cells were harvested and analyzed for luciferase activity. The experiment was repeated three times in triplicate.
- Citation: Ku HJ, Kim HY, Kim HH, Park HJ, Cheong JH. Bile acid increases expression of the histamine-producing enzyme, histidine decarboxylase, in gastric cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 175-182
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/175.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.175