Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2013; 19(9): 1451-1457
Published online Mar 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i9.1451
Published online Mar 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i9.1451
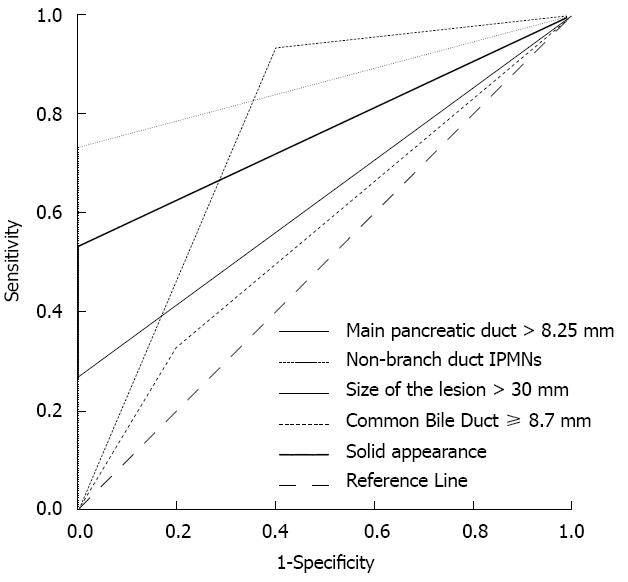
Figure 1 Characteristics of computed tomography/magnetic resonance imaging.
Receiver operating characteristic analysis showed that non-branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), lesion size > 30 mm and a solid component appearance in the lesion had great significance for predicting pancreatic resection, and the area under the curve reached 0.76 (P = 0.012, 95%CI: 0.569-0.964), 0.867 (P = 0.001, 95%CI: 0.758-0.976) and 0.76 (P < 0.01, 95%CI: 0.623-0.910), respectively.
- Citation: Xu B, Ding WX, Jin DY, Wang DS, Lou WH. Decision making for pancreatic resection in patients with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(9): 1451-1457
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i9/1451.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i9.1451