Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2013; 19(6): 846-854
Published online Feb 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i6.846
Published online Feb 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i6.846
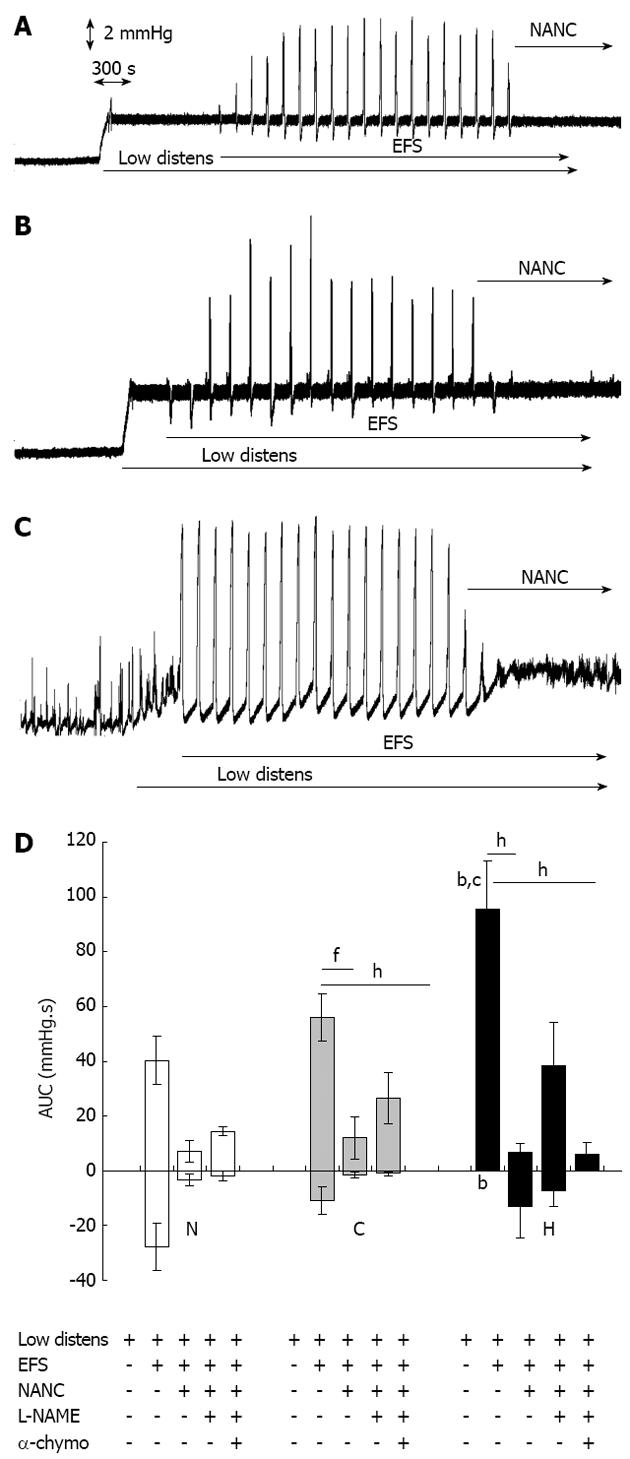
Figure 2 Motor responses to electrical field stimulation.
Original tracings representing changes of intraluminal pressure of ileal segments in basal conditions and following subsequent application of a hydrostatic pressure of 5 cm H2O (Low distens), EFS (30 V, 1 ms, 3 Hz, trains lasting 20 s every 120 s) and NANC conditions (NANC). A: Normal tissues; B: Control tissues; C: Hypertrophic tissues; D: Area under the pressure-time curve of motor responses in normal (N), control (C) and hypertrophic (H) ileal segments following subsequent application of a hydrostatic pressure of 5 cm H2O (Low distens), EFS (30 V, 1 ms, 3 Hz, trains lasting 20 s every 120 s), NANC conditions (NANC), incubation with L-NAME 300 μmol/L (L-NAME) and incubation with α-chymotrypsin 10 IU/mL (α-chymo). Each value is the mean ± SE of 5 distinct experiments per group. bP < 0.01 vs corresponding normal values; cP < 0.05 vs corresponding control values; fP < 0.01; hP < 0.001; analysis of variance test followed by Bonferroni’s post-test.
- Citation: Bertoni S, Saccani F, Gatti R, Rapalli A, Flammini L, Ballabeni V, Barocelli E. Accommodation and peristalsis are functional responses to obstruction in rat hypertrophic ileum. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(6): 846-854
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i6/846.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i6.846