Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2013; 19(5): 682-691
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.682
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.682
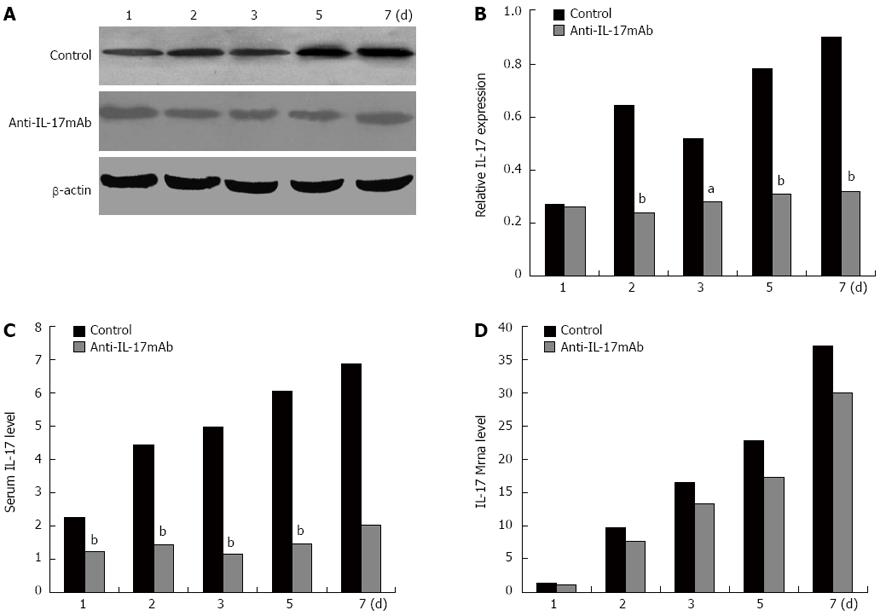
Figure 5 Expression of interleukin-17 in rat intestine and serum after transplantation.
The intestines from inbred F344 were transplanted to LEW rats. The recipient rats were randomly divided into control and anti-interleukin (IL)-17 monoclonal antibody (mAb) treated groups. The rats were sacrificed on the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 5th, and 7th d after transplantation. A: Western blot analysis of graft proteins of different groups. β-actin were considered as an internal control; B: The bands were scanned and the protein expressions were analyzed with Band Scan software; C: Blood from the heart was extracted and the serum IL-17 levels was detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; D: The mRNA of IL-17 was detected by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. β-actin was considered as an internal control. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group.
- Citation: Yang JJ, Feng F, Hong L, Sun L, Li MB, Zhuang R, Pan F, Wang YM, Wang WZ, Wu GS, Zhang HW. Interleukin-17 plays a critical role in the acute rejection of intestinal transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(5): 682-691
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i5/682.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.682