Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2013; 19(5): 673-681
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.673
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.673
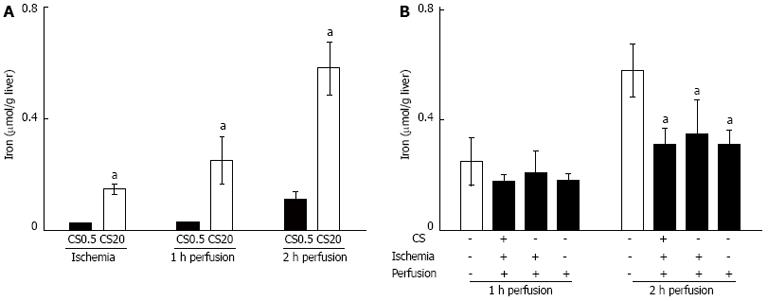
Figure 4 Iron release during warm ischemia and perfusion and effect of desferrioxamine on iron release.
A: Iron release was measured in media after warm ischemia (WI) and at 1 and 2 h of perfusion from the control livers after 0.5 h of cold storage (CS0.5) and from the livers after 20 h of extended cold storage (CS20). Significantly different from the controls (mean ± SE, n = 5, aP < 0.05); B: Iron release was measured in media at 1 and 2 h of perfusion from livers following 20 h of cold storage (CS). Addition of desferrioxamine (DFO) to CS, WI and perfusion media is indicated by (+). Significantly different from 20 h of CS with no DFO (mean ± SE, n = 5, aP < 0.05).
- Citation: Arthur PG, Niu XW, Huang WH, DeBoer B, Lai CT, Rossi E, Joseph J, Jeffrey GP. Desferrioxamine in warm reperfusion media decreases liver injury aggravated by cold storage. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(5): 673-681
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i5/673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.673