Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2013; 19(5): 673-681
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.673
Published online Feb 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.673
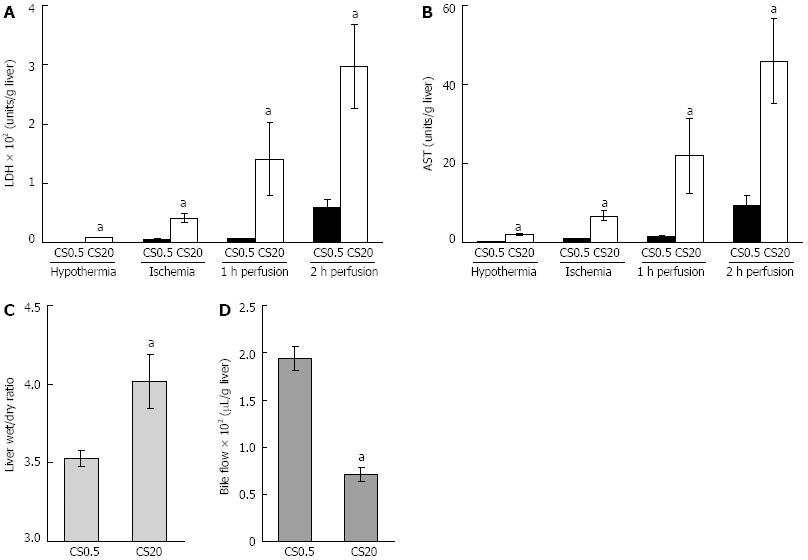
Figure 1 Liver function following cold storage, warm ischemia and perfusion.
A, B: Liver damage was assessed by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in media from control livers after 0.5 h of cold storage (CS0.5) and from the livers after 20 h of extended cold storage (CS20). LDH and AST were measured in media flushed from livers following cold storage, in media flushed from livers following 25 min of warm ischemia and in media at 1 and 2 h of warm perfusion; C, D: Liver health was assessed by liver swelling (liver wet to dry ratio) after 2 h of perfusion and bile flow over 2 h of perfusion. Significantly different from the controls (mean ± SE, n = 5, aP < 0.05).
- Citation: Arthur PG, Niu XW, Huang WH, DeBoer B, Lai CT, Rossi E, Joseph J, Jeffrey GP. Desferrioxamine in warm reperfusion media decreases liver injury aggravated by cold storage. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(5): 673-681
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i5/673.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.673