Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2013; 19(48): 9240-9255
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240
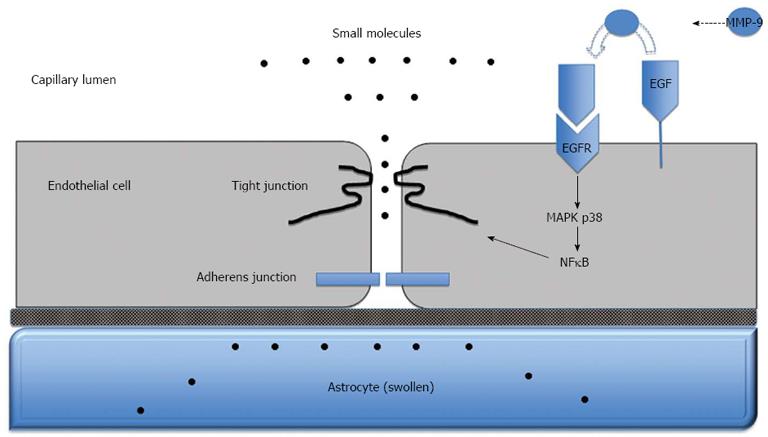
Figure 3 Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in acute liver failure.
Anatomy of the blood-brain barrier (BBB) created by the brain capillary endothelial cell and its paracellular tight junction and adherens junction. In acute liver failure, activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and other signaling pathways results in a loss of BBB tight junction integrity. Tight junctional proteins are altered, resulting in increased permeability to small molecules, leading to astrocyte swelling. MMP-9: Matrix metalloproteinase-9; MAPK p38: Mitogen activated protein kinase p38; NFκB: Nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Scott TR, Kronsten VT, Hughes RD, Shawcross DL. Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(48): 9240-9255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i48/9240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240