Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2013; 19(48): 9240-9255
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240
Published online Dec 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240
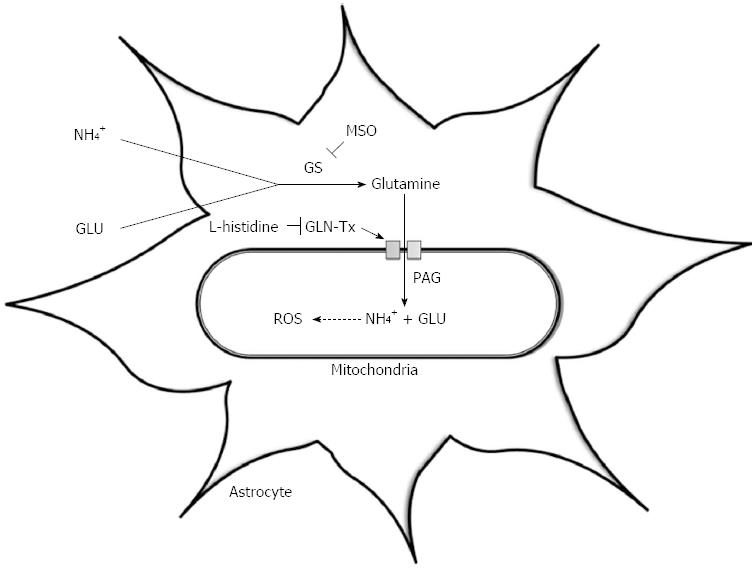
Figure 1 The ‘Trojan Horse’ hypothesis.
This illustrates the synthesis of glutamine via the enzyme glutamine synthetase; its transport into mitochondria via the glutamine transporter (GLN-Tx); its hydrolysis by phosphate-activated glutaminase (PAG) resulting in glutamate (GLU) and ammonia (NH4+) production and the subsequent generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). MSO: L-methionine S-sulfoximinel; GS: Glutamine synthetase.
- Citation: Scott TR, Kronsten VT, Hughes RD, Shawcross DL. Pathophysiology of cerebral oedema in acute liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(48): 9240-9255
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i48/9240.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9240