Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2013; 19(47): 9069-9076
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9069
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9069
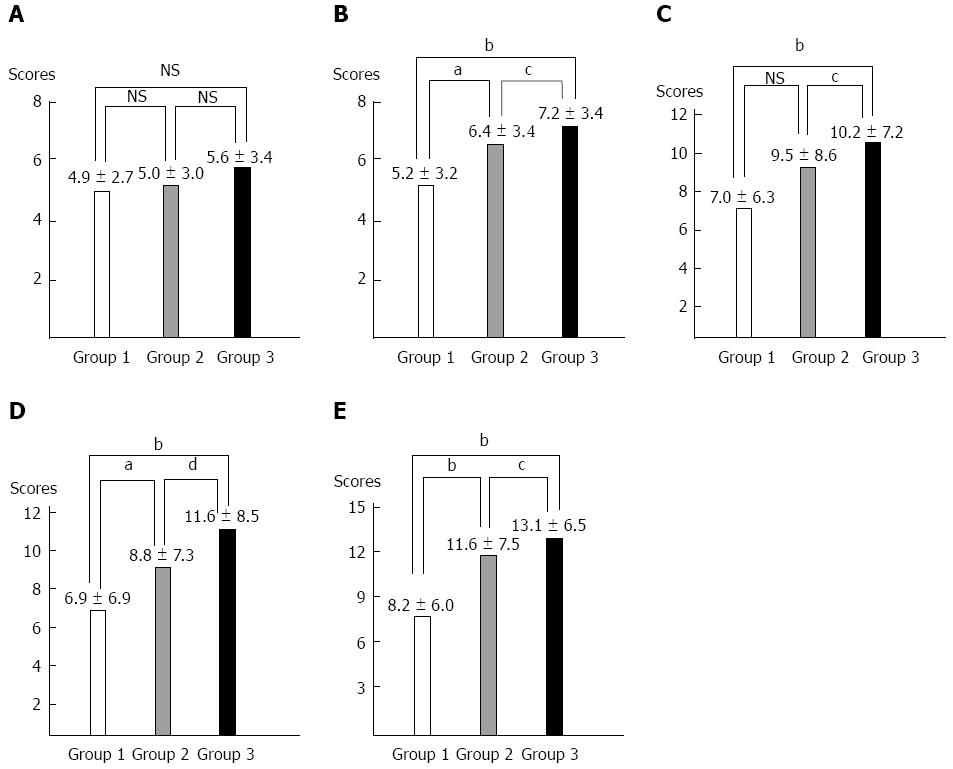
Figure 1 The anxiety and depression subscale of the Hospital Anxiety-Depression Scale, Beck anxiety inventory, Beck depression inventory and the hypochondriasis scores among the study groups.
A: Group 3 showed the highest score, but there was no significant difference in the HADS anxiety subscale between groups; B: The HADS depression subscale in Group 3 showed the most significant score; C: The BAI in Group 3 showed the most significant score; D: The BDI in Group 3 showed the most significant score; E: Group 3 showed a significantly higher hypochondriasis score. Group 1: Control group; Group 2: Non-toxic acute liver injury group; Group 3: Toxic acute liver injury group involving toxic hepatitis. NS: Non significant; HADS: Hospital Anxiety-Depression Scale; BAI: Beck anxiety inventory; BDI: Beck depression inventory. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs Group 1; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs Group 2. P value by the Mann-Whitney U test.
- Citation: Suh JI, Sakong JK, Lee K, Lee YK, Park JB, Kim DJ, Seo YS, Lee JD, Ko SY, Lee BS, Kim SH, Kim BS, Kim YS, Lee HJ, Kim IH, Sohn JH, Kim TY, Ahn BM. Anxiety and depression propensities in patients with acute toxic liver injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(47): 9069-9076
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i47/9069.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9069