Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2013; 19(47): 8895-8901
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8895
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8895
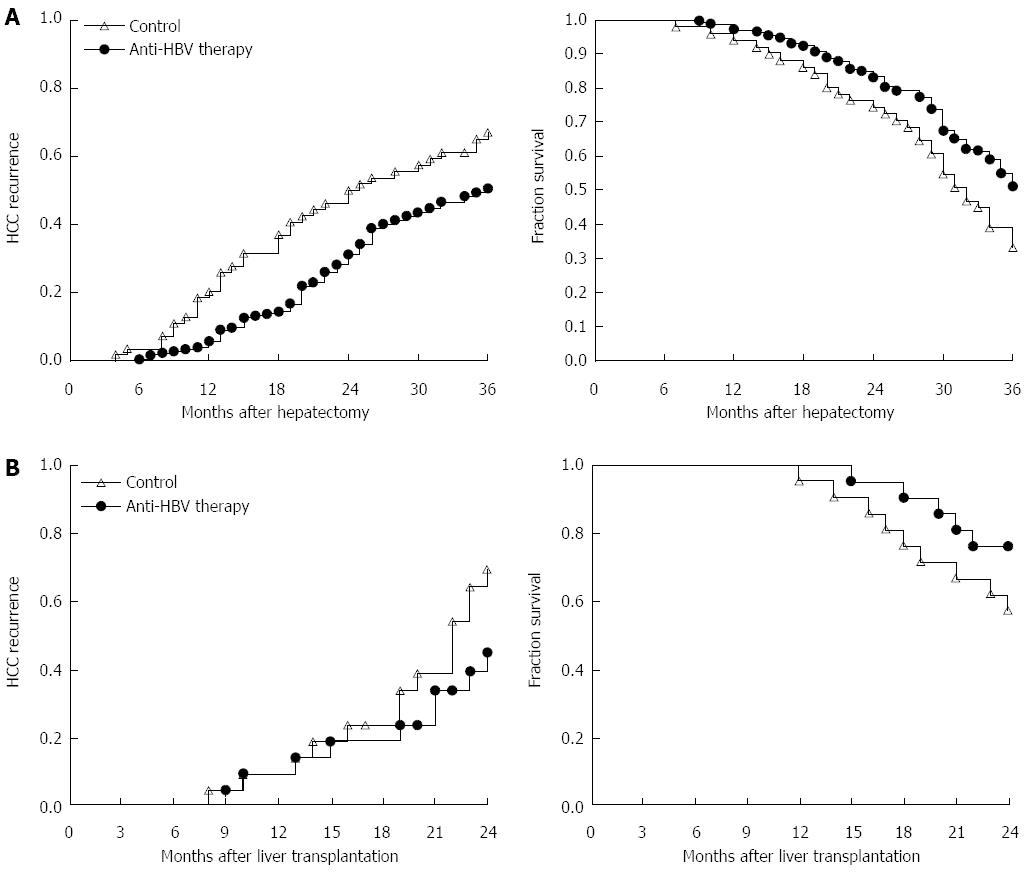
Figure 1 Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence and outcome in patients who received anti-hepatitis B virus therapy or placebo after hepatectomy or liver transplantation.
A: From September 2009 to May 2010, 224 HCC patients who received partial hepatectomy due to HBV-related HCC were enrolled. HCC recurrence and 3-year overall survival rate in patients with anti-HBV treatment (n = 173) and patients without standardized anti-HBV treatment (n = 51) were monitored for at least 3 years. Left: log-rank test, P = 0.013; right: log-rank test, P = 0.006; B: From January 2010 to August 2011, 42 HCC patients within Milan criteria who received liver transplantation were enrolled. HCC recurrence and 2-year overall survival rate in patients with anti-HBV treatment (n = 28) and patients without standardized anti-HBV treatment (n = 14) are shown. Left: log-rank test, P = 0.031; right: log-rank test, P = 0.045. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Tan ZM, Sun BC. Effects of antiviral therapy on preventing liver tumorigenesis and hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(47): 8895-8901
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i47/8895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8895