Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2013; 19(45): 8269-8281
Published online Dec 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8269
Published online Dec 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8269
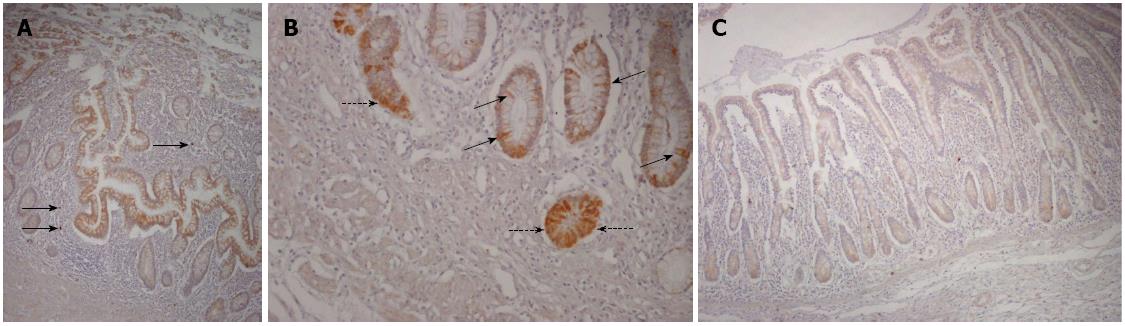
Figure 2 Receptor for the advanced glycation end products staining in Crohn’s disease and healthy mucosa.
A: Almost all cells of the epithelial compartment at both crypt and surface levels showed positive immunostaining (brown cells) in a representative case of Crohn’s disease affected areas, with only a few scattered positive cells in the lamina propria (black arrows); B: The pattern of the cellular staining in the crypt zone of a representative case of Crohn’s disease affected area is shown, indicating both membranous and cytosolic distribution; C: A representative case of control mucosa is shown, with weak staining of the epithelial cells and only a few scattered positive cells in the lamina propria (receptor for the advanced glycation end products, immunoperoxidase-hematoxylin; original magnification, × 200).
- Citation: Ciccocioppo R, Vanoli A, Klersy C, Imbesi V, Boccaccio V, Manca R, Betti E, Cangemi GC, Strada E, Besio R, Rossi A, Falcone C, Ardizzone S, Fociani P, Danelli P, Corazza GR. Role of the advanced glycation end products receptor in Crohn’s disease inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(45): 8269-8281
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i45/8269.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8269