Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2013; 19(44): 8056-8064
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.8056
Published online Nov 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.8056
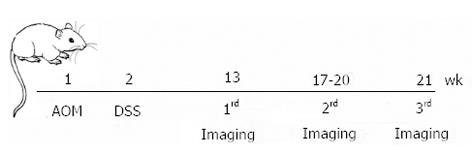
Figure 1 Schematic overview of the azoxymethane and dextran sulfate sodium model and subsequent image acquisition.
A single azoxymethane (AOM) ip injection was given to 6-wk-old mice (week 1). One week later (week 2), 3% dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) administration was given in the drinking water for 7 d, followed by regular water. The first endoluminal ultrasonic biomicroscopy (eUBM) and colonoscopic images were acquired at week 13, the second acquisition was from weeks 17-20, and the third acquisition was at week 21.
- Citation: Soletti RC, Alves KZ, Britto MA, Matos DG, Soldan M, Borges HL, Machado JC. Simultaneous follow-up of mouse colon lesions by colonoscopy and endoluminal ultrasound biomicroscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(44): 8056-8064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i44/8056.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i44.8056