Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2013; 19(43): 7586-7593
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7586
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7586
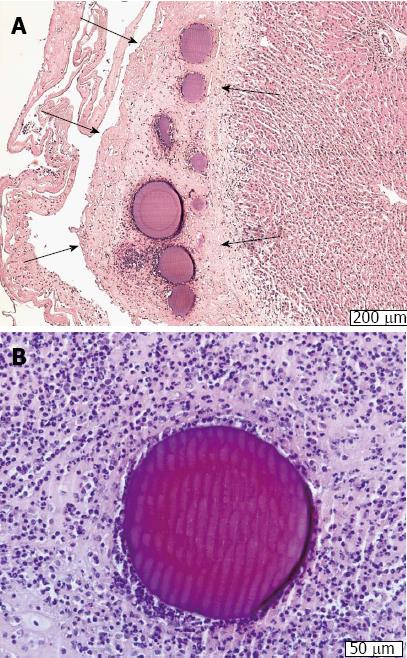
Figure 2 Doxorubicin-eluting beads.
A: HE-stained, magnification × 50: A layer of fibrin (between arrows) immobilizing the doxorubicin-loaded DC beads (DOXDEB™) on the livers surface; B: HE-stained, magnification × 100: DOXDEB™ in layer of fibrin and surrounded by lymphocytes immobilizing it on mesenteric connective tissue.
- Citation: Binder S, Lewis AL, Löhr JM, Keese M. Extravascular use of drug-eluting beads: A promising approach in compartment-based tumor therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(43): 7586-7593
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i43/7586.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7586