Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2013; 19(43): 7569-7576
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7569
Published online Nov 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7569
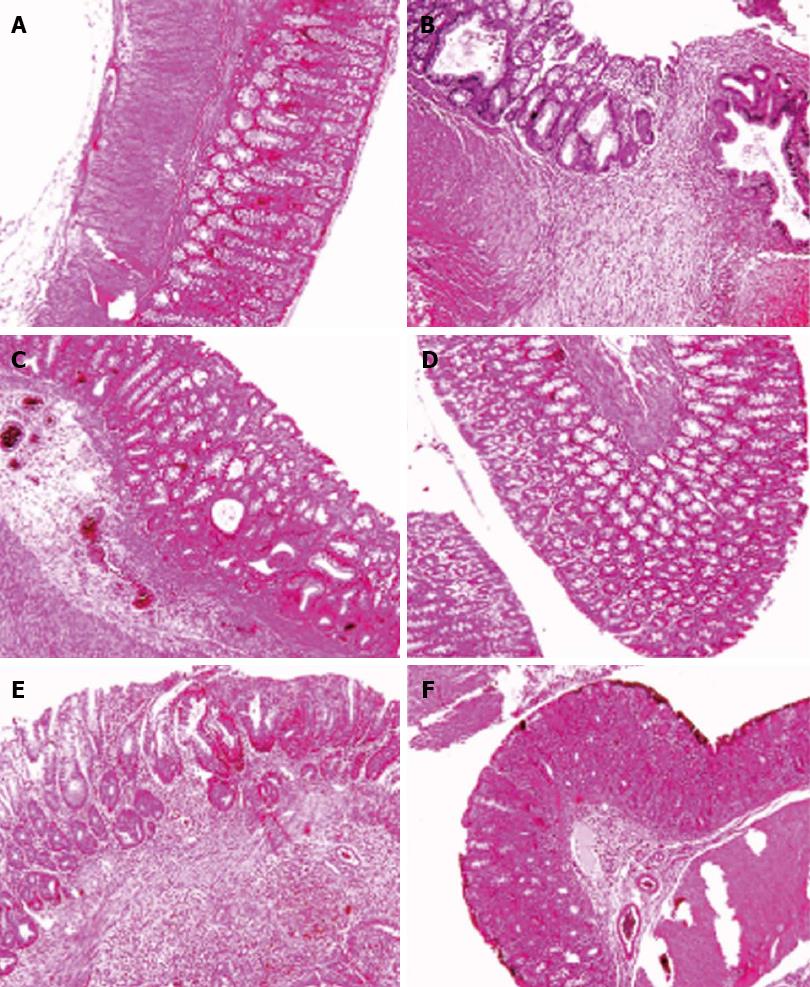
Figure 3 Histological images of colon tissues obtained from different groups.
Microscopic evaluation of the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS) group shows villus atrophy, extensive severe transmural inflammation, granuloma with necrosis and crypt destruction, whereas features in the Sham group were normal. Histological examination of the Ethanol group showed a mild crypt distortion and some crypt abscess, whereas features in the Vaccine group were normal. Microscopic evaluation of the Model group showed mucosal inflammation and crypt distortion, branching and some ulceration with moderate to severe crypt destruction in ulcerated regions. Mild focal inflammation, minimal inflammatory cell infiltration and slight crypt branching were observed in the Infliximab group. A: Sham; B: TNBS; C: Ethanol; D: Vaccine; E: Model; F: Infliximab.
- Citation: Esmaily H, Sanei Y, Abdollahi M. Autoantibodies and an immune-based rat model of inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(43): 7569-7576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i43/7569.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i43.7569