Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2013; 19(42): 7440-7446
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7440
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7440
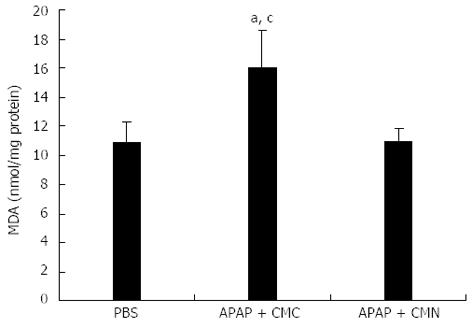
Figure 2 Curcumin pretreatment inhibits malondialdehyde production after acetaminophen induction.
Liver homogenate was prepared to analyze the content of malondialdehyde (MDA) 16 h after acetaminophen (APAP) administration. Data are expressed as mean ± SE; n = 10 mice per group. aP < 0.05 vs control; cP < 0.05 vs APAP + curcumin (CMN). CMC: Carboxymethylcellulose.
- Citation: Li G, Chen JB, Wang C, Xu Z, Nie H, Qin XY, Chen XM, Gong Q. Curcumin protects against acetaminophen-induced apoptosis in hepatic injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(42): 7440-7446
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i42/7440.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7440