Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2013; 19(42): 7374-7388
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374
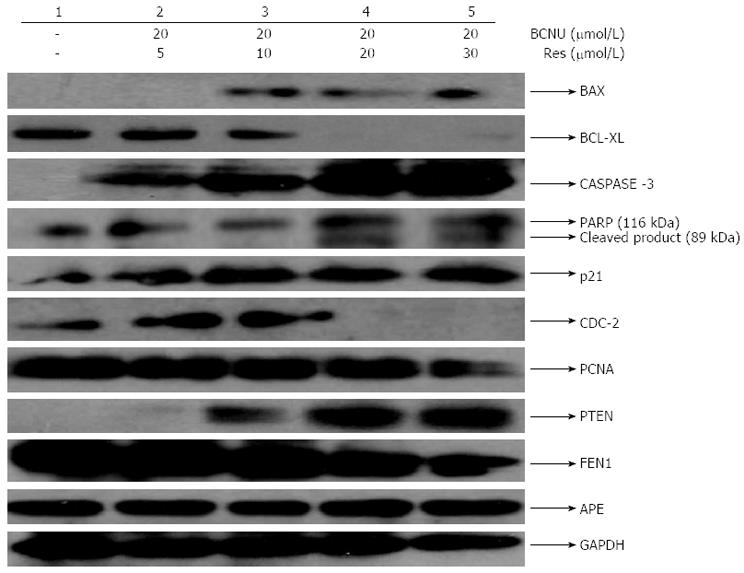
Figure 3 Combined effects of 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and resveratrol on various cellular markers in HCT-116 colon cancer cells.
Expression pattern of apoptotic, DNA damage/repair and cell cycle regulatory proteins after drug treatment. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as a loading control. BAX: Bcl-2-associated X protein; BCL-XL: B-cell lymphoma-extra large; PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; FEN1: Flap endonuclease 1; CDC-2: Cyclin dependent kinase-1; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea; APE: Apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease.
- Citation: Das D, Preet R, Mohapatra P, Satapathy SR, Kundu CN. 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea enhances the inhibitory effect of Resveratrol on 5-fluorouracil sensitive/resistant colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(42): 7374-7388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i42/7374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374