Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2013; 19(42): 7374-7388
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374
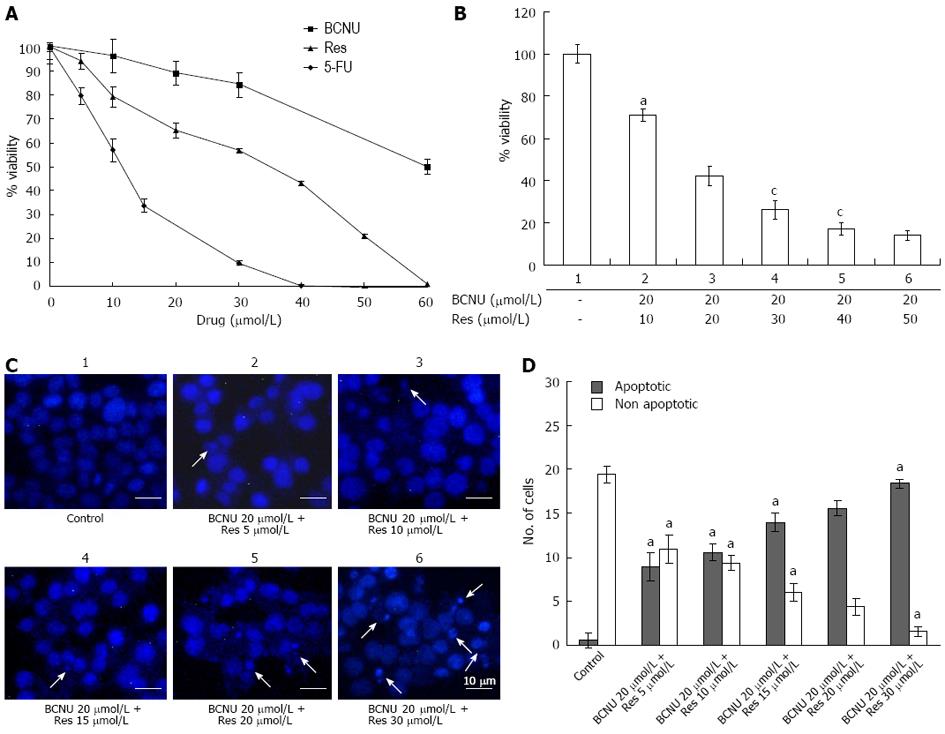
Figure 1 Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and/or resveratrol on HCT-116 colon cancer cells.
A: Anchorage-dependent cell survival of HCT-116 cells after treatment with Res, 5-FU and BCNU; B: Bar diagram representing the % viability of HCT-116 after BCNU+ Res exposure. HCT-116 cells were cultured in 96 well plates and grown to 60%-70% confluence. The cells were then treated with different compounds according to the materials and methods. Data are the mean ± SD of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 20 μmol/L Res; cP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 50 μmol/L Res; C: Apoptotic nuclei after 4',6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole hydrochloride staining. Images were taken using a fluorescent microscope (Nikon-Eclipse, Japan) at × 40 magnification. Arrows indicate the apoptotic nuclei. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; D: A graphical representation of apoptotic nuclei. aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 20 μmol/L Res. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea.
- Citation: Das D, Preet R, Mohapatra P, Satapathy SR, Kundu CN. 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea enhances the inhibitory effect of Resveratrol on 5-fluorouracil sensitive/resistant colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(42): 7374-7388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i42/7374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374