Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2013; 19(40): 6869-6875
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6869
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6869
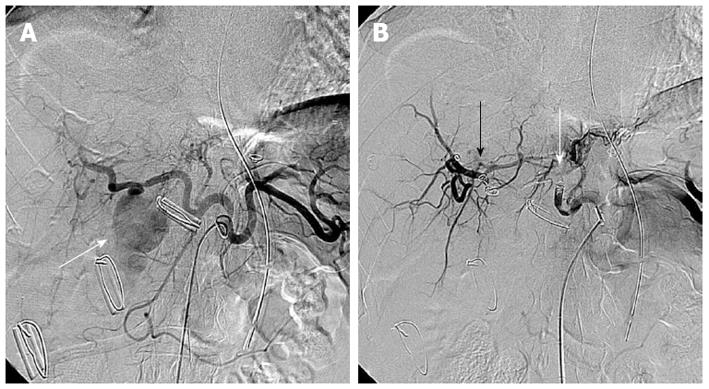
Figure 2 A 56-year-old man presented with massive bleeding from surgical drains after choledocholithotomy due to common bile duct stone.
A: Selective celiac arteriography showed a pseudoaneurysm (arrow) arising from the right hepatic artery; B: Selective celiac arteriography after embolization with microcoils and gelfoam demonstrated disappearance of the pseudoaneurysm. Embolic agents were inserted proximally (white arrow) and distally (black arrow) to the origin of the pseudoaneurysm.
- Citation: Zhou CG, Shi HB, Liu S, Yang ZQ, Zhao LB, Xia JG, Zhou WZ, Li LS. Transarterial embolization for massive gastrointestinal hemorrhage following abdominal surgery. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(40): 6869-6875
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i40/6869.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6869