Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2013; 19(40): 6814-6824
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6814
Published online Oct 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6814
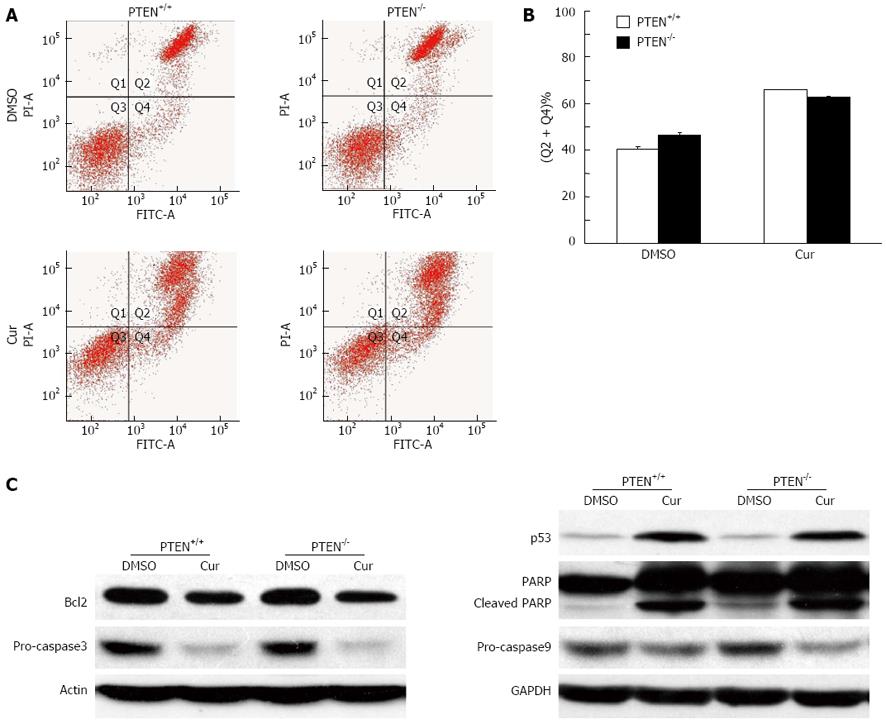
Figure 4 PTEN deficiency does not enhance curcumin-induced apoptosis.
A: Images showing flow cytometric analysis of apoptosis. Apoptosis was analyzed by flow cytometry with the Annexin V-FITC kit; B: Histograms showing apoptosis assay results. Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) deletion did not result in increased apoptosis following curcumin treatment; C: Western blotting analysis. Cell lysates were separated on SDS-PAGE, transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes, and incubated with indicated antibodies. Cur: Curcumin; PI: Propidium iodide; FITC: Fluorescein isothiocyanate; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Chen L, Li WF, Wang HX, Zhao HN, Tang JJ, Wu CJ, Lu LT, Liao WQ, Lu XC. Curcumin cytotoxicity is enhanced by PTEN disruption in colorectal cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(40): 6814-6824
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i40/6814.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i40.6814