Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 28, 2013; 19(4): 492-502
Published online Jan 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492
Published online Jan 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492
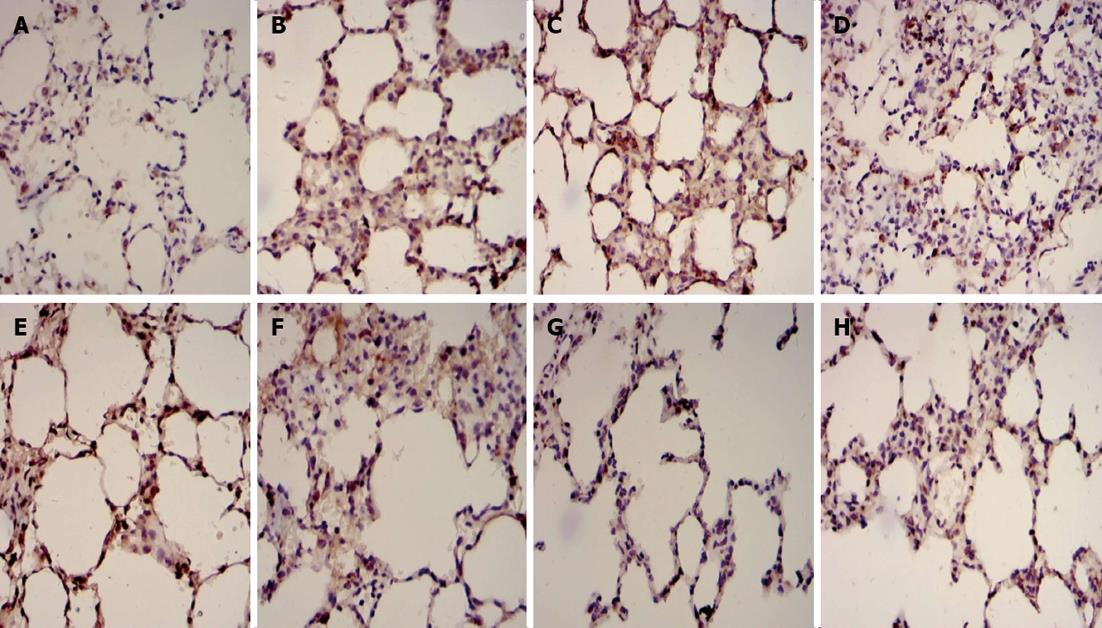
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical examples for Fas and Bcl2 in dorsal lobe of right lung tissue.
A: Fas in control group; B: Fas in septic shock group; C: Fas in early fluid resuscitation-treated group; D: Fas in early fluid resuscitation + 2% hydrogen inhalation-treated group; E: Bcl2 in control group; F: Bcl2 in septic shock group; G: Bcl2 in early fluid resuscitation-treated group; H: Bcl2 in early fluid resuscitation + 2% hydrogen inhalation-treated group. Examples were examined under a light microscope equipped with an image analysis system. Yellow or brownish-yellow staining represents positive staining. The expression of Fas proteins was up-regulated, while the expression of Bcl2 proteins was down-regulated in Group B compared with Group A. In Group C, however, the expression of Fas proteins was down-regulated, and the expression of Bcl2 proteins was up-regulated compared with Group B. In addition, the lower expression of Fas proteins and the higher expression of Bcl2 proteins were observed in Group D compared with Group C.
- Citation: Liu W, Shan LP, Dong XS, Liu XW, Ma T, Liu Z. Combined early fluid resuscitation and hydrogen inhalation attenuates lung and intestine injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(4): 492-502
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i4/492.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.492