Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2013; 19(37): 6265-6271
Published online Oct 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6265
Published online Oct 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6265
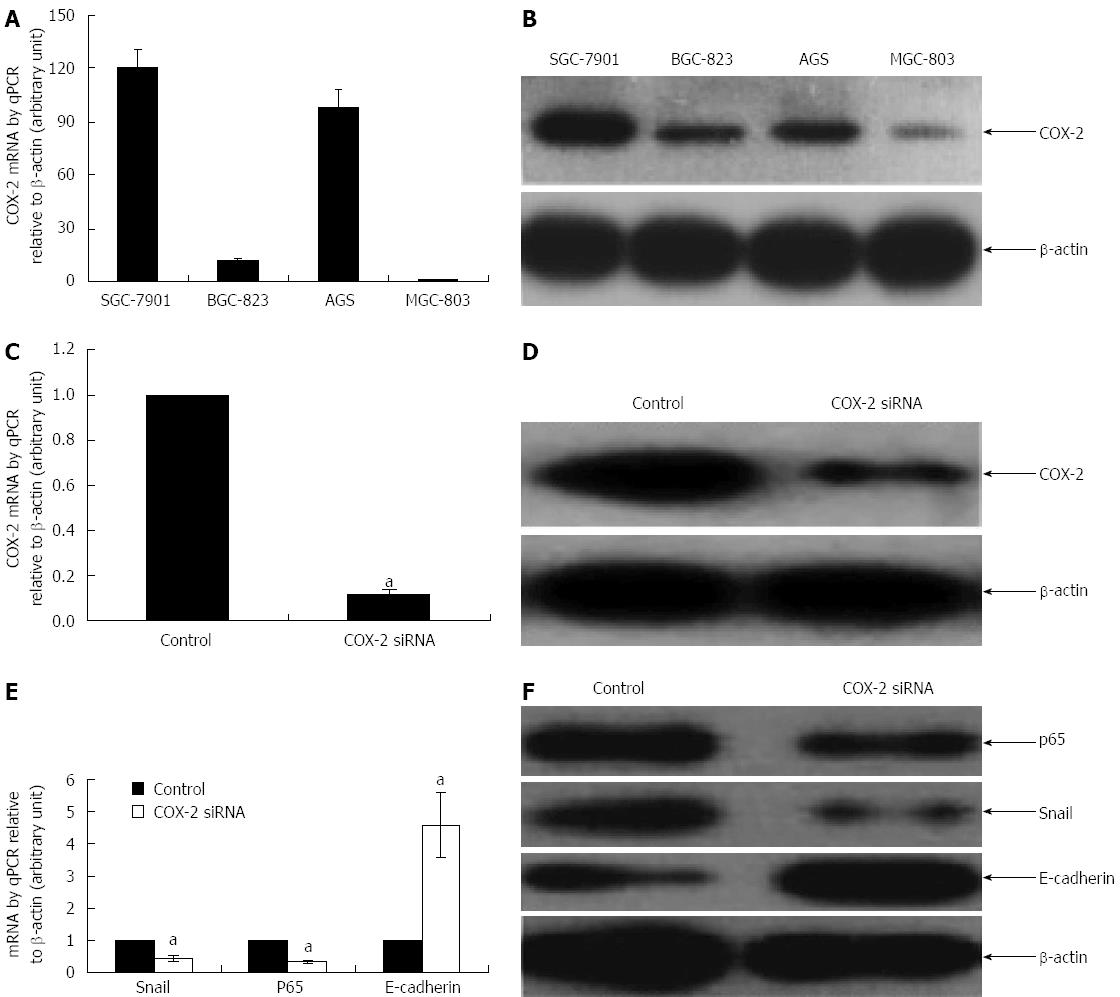
Figure 1 Effect of cyclooxygenase-2 knockdown on the expression of nuclear factor-κB, Snail, and E-cadherin in gastric cancer cells.
Among the four human gastric cancer cell lines, SGC-7901 has the highest expression level of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) at mRNA (A) and protein level (B). Thus, this cell line was used to study the regulatory effect of COX-2 on nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), Snail, and E-cadherin. Successful knockdown of COX-2 was confirmed at mRNA (C) and protein (D) levels. Down-regulation of COX-2 led to a reduction of NF-κB subunit p65 and Snail but an increased E-Cadherin, both at the mRNA (E) and protein (F) levels. mRNA expression was examined by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and expressed as a relative arbitrary unit against that of β-actin. Protein expression was examined by Western blot (aP < 0.05 vs their respective controls).
- Citation: Liu XJ, Chen ZF, Li HL, Hu ZN, Liu M, Tian AP, Zhao D, Wu J, Zhou YN, Qiao L. Interaction between cyclooxygenase-2, Snail, and E-cadherin in gastric cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(37): 6265-6271
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i37/6265.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6265