Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2013; 19(37): 6228-6236
Published online Oct 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6228
Published online Oct 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6228
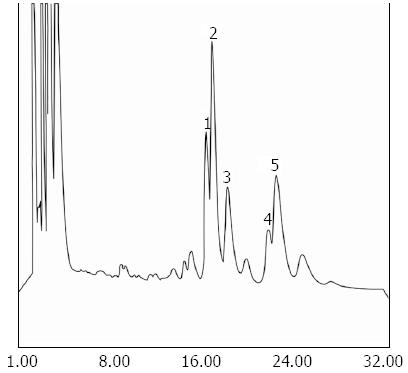
Figure 3 A typical high-performance liquid chromatography chromatogram of a liver homogenate.
Phospholipids were separated by thin layer chromatography (TLC) and the phosphatidylcholine band was scraped off the TLC plate and extracted with 2 × 1 mL methanol [high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) grade]. After determination of the phospholipid, 20 nmol was injected onto HPLC for the analysis of the fatty acid composition of the phosphatidylcholine as described in the methods section. Results are presented as mean ± SE (n = 6). A typical chromatogram is presented. Peak 1: Not identified; peak 2: 1-palmitoyl 2-arachidonyl (16:0-20:4) phosphatidylcholine; peak 3: 1-palmitoyl 2-linoleyl (16:0-18:2) phosphatidylcholine; peak 4: 1-palmitoyl 2-oleoyl (16:0-18:1) phosphatidylcholine; peak 5: 1-stearol 2-arachidonyl (18:0-20:4) phosphatidylcholine.
- Citation: Hismiogullari AA, Hismiogullari SE, Rahman K. Isolation and biochemical analysis of vesicles from taurohyodeoxycholic acid-infused isolated perfused rat livers. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(37): 6228-6236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i37/6228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i37.6228