Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2013; 19(36): 5988-5999
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.5988
Published online Sep 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.5988
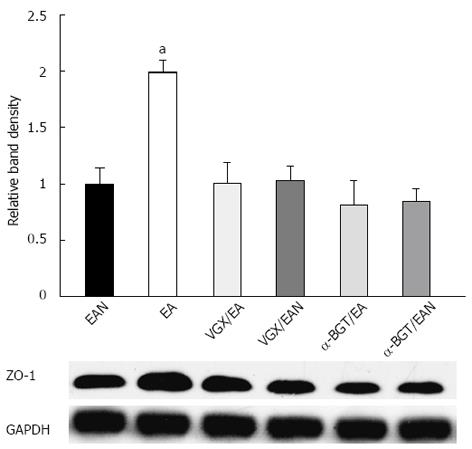
Figure 7 Intestinal ZO-1 protein expression at 12 h after blood loss.
Intestinal extracts were obtained from animals at 12 h after blood loss for measurement of ZO-1 protein expression using Western blotting. Representative Western blotting for the ZO-1 protein is shown with its corresponding glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase loading control to demonstrate equal protein load in all lanes. Electroacupuncture at ST36 resulted in preservation of protein expression. Significant reduction in ZO-1 expression was seen in all the other groups. aP < 0.05 vs EAN group, (3-5 animals per group at 12h after blood loss). EA: Electroacupuncture; VGX: Vagotomy; α-BGT: α-bungarotoxin; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Du MH, Luo HM, Hu S, Lv Y, Lin ZL, Ma L. Electroacupuncture improves gut barrier dysfunction in prolonged hemorrhagic shock rats through vagus anti-inflammatory mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(36): 5988-5999
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i36/5988.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i36.5988