Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2013; 19(34): 5713-5719
Published online Sep 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5713
Published online Sep 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5713
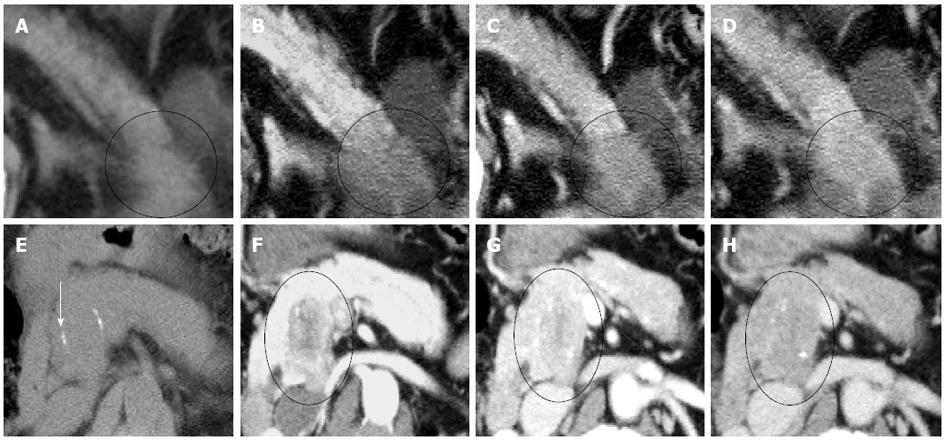
Figure 3 Visual patterns of the adenocarcinoma and the acinar cell carcinoma in the 4 phases.
A-D: Adenocarcinoma in the pancreatic tail (circle); The tumor was hypodense in all 4 phases (A: Non-contrast phase; B: Arterial phase; C: Portal venous phase; D: delayed phase). It showed a gradual enhancement pattern across the phases; E-H: Case 1, Acinar cell carcinoma in the pancreatic head (circle); The tumor was isodense and undetectable in the non-contrast phase, although calcification was identified (arrow) (E); It was hypodense in all 3 contrast-enhanced phases (F: Arterial phase; G: Portal venous phase; H: Delayed phase); Contrast enhancement was the strongest in the portal venous phase (G).
- Citation: Sumiyoshi T, Shima Y, Okabayashi T, Kozuki A, Nakamura T. Comparison of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma using multidetector-row computed tomography. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(34): 5713-5719
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i34/5713.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i34.5713