Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2013; 19(33): 5500-5507
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5500
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5500
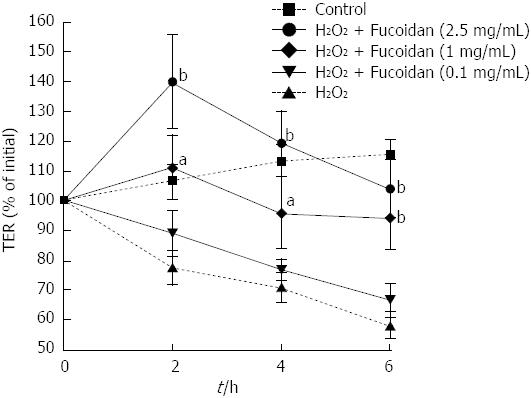
Figure 2 Fucoidan prevented H2O2-induced destruction of intestinal epithelial barrier function in a dose-dependent manner.
Polarized Caco-2 cell monolayers were injured by H2O2 (500 μmol/L) on the apical side of Caco-2 cell monolayers. Fucoidan was added into the basolateral side 30 min prior to H2O2 stimulation and cultured for 6 h. Changes in intestinal epithelial barrier function were monitored by measuring the trans-epithelial resistance (TER). The data are expressed as the means ± SEM of 5 independent experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 compared with cells exposed to H2O2 alone at respective time point (Tukey’s multiple comparison test).
- Citation: Iraha A, Chinen H, Hokama A, Yonashiro T, Kinjo T, Kishimoto K, Nakamoto M, Hirata T, Kinjo N, Higa F, Tateyama M, Kinjo F, Fujita J. Fucoidan enhances intestinal barrier function by upregulating the expression of claudin-1. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(33): 5500-5507
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i33/5500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5500