Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2013; 19(33): 5485-5492
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5485
Published online Sep 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5485
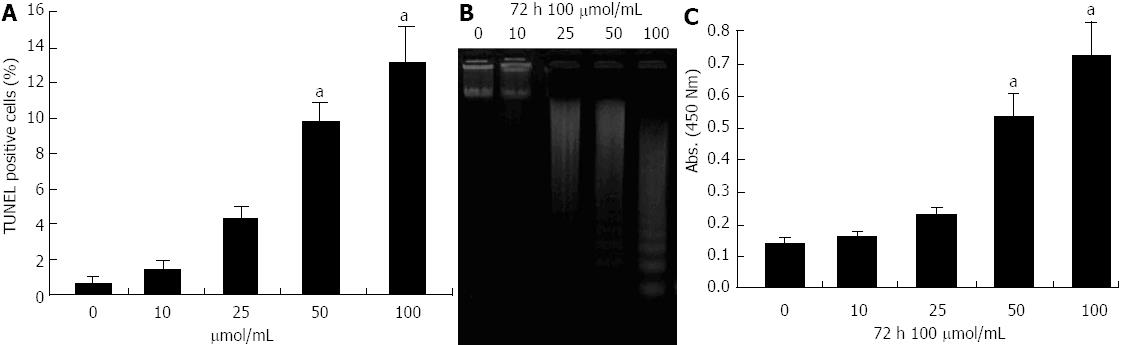
Figure 2 Evaluation of apoptosis of pancreatic cancer MIA-PaCa-2 cells after propofol treatment using terminal transferase dUTP nick-end labeling, DNA ladder and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays.
A: Propofol-induced apoptotic cell death by terminal transferase dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) after 72 h of 10-100 μmol/L propofol; B: DNA ladder indicative of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells treated with 10-100 μmol/mL propofol for 72 h. C: Propofol-induced apoptosis measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay after 72 h of 10-100 μmol/L propofol. aP < 0.05 vs control group.
-
Citation: Du QH, Xu YB, Zhang MY, Yun P, He CY. Propofol induces apoptosis and increases gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer cells
in vitro by inhibition of nuclear factor-κB activity. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(33): 5485-5492 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i33/5485.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i33.5485