Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2013; 19(32): 5250-5260
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5250
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5250
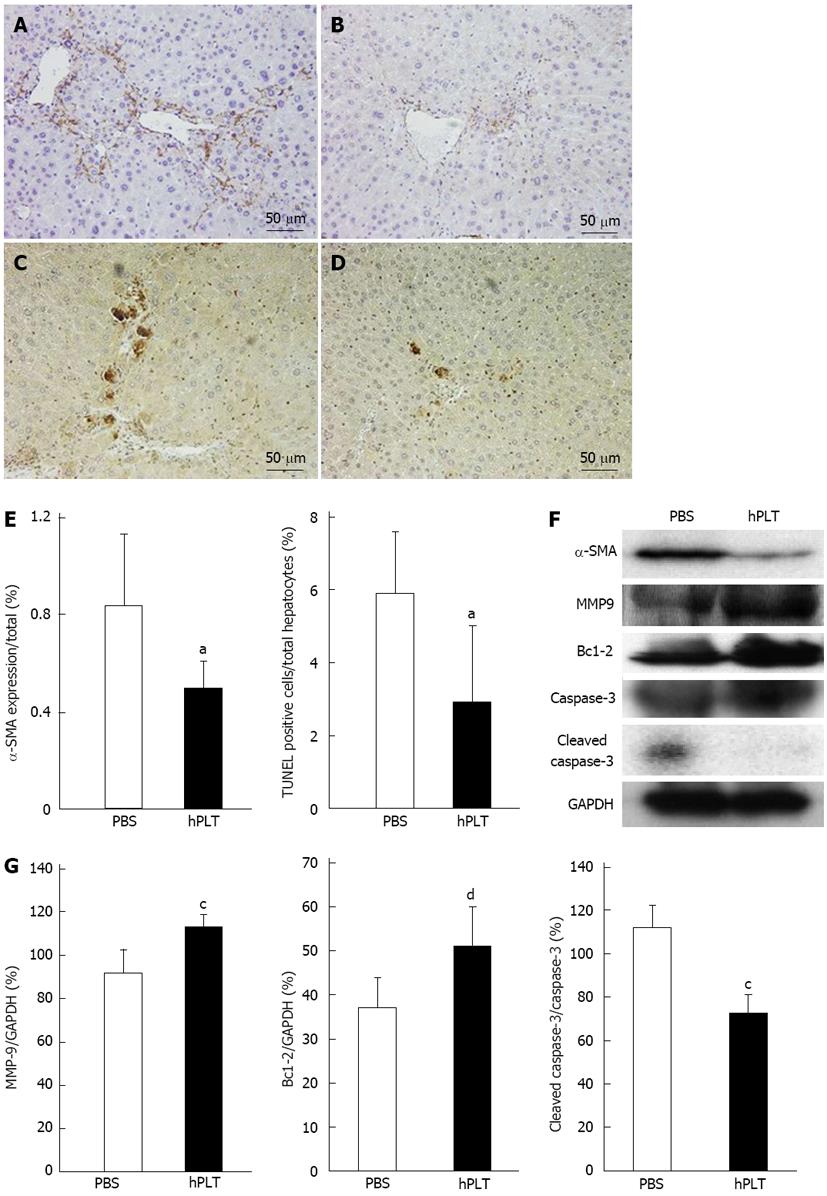
Figure 4 α-smooth muscle actin and TUNEL staining.
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9), Bcl-2, caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3 expression levels. A, B: Immunostaining of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) in the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS group) or human platelet transfusions (hPLT group). The α-SMA staining was less robust in the hPLT group than in the PBS group; C, D: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining in the PBS and hPLT groups. Few apoptotic cells were observed in the hPLT group, whereas several apoptotic hepatocytes were observed in the PBS group; E: α-SMA expression calculated based on the area stained by anti-α-SMA antibody and TUNEL-positive hepatocytes/total hepatocytes in the PBS and hPLT groups. n = 6 per group. Data are expressed as the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05 using an unpaired t-test. α-SMA expression and the number of apoptotic hepatocytes in the hPLT group were lower than those in the PBS group; F: α-SMA, MMP-9, Bcl-2, caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-3 expression levels assessed with Western blotting. α-SMA and cleaved caspase-3 expression levels were less intense in the hPLT group than in the PBS group, whereas MMP-9 and Bcl-2 expression levels were stronger in the hPLT group than in the PBS group; G: MMP-9, Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase-3 expression levels were quantified using densitometry. n = 3 per group. Data are expressed as the means ± SD. cP < 0.05 and dP < 0.01 using an unpaired t-test. MMP-9 and Bcl-2 expression levels were significantly higher in the hPLT group than in the PBS group, whereas cleaved caspase-3 expression was significantly lower in the hPLT group than in the PBS group. Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma-2.
- Citation: Takahashi K, Murata S, Fukunaga K, Ohkohchi N. Human platelets inhibit liver fibrosis in severe combined immunodeficiency mice. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(32): 5250-5260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i32/5250.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5250