Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2013; 19(32): 5238-5249
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5238
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5238
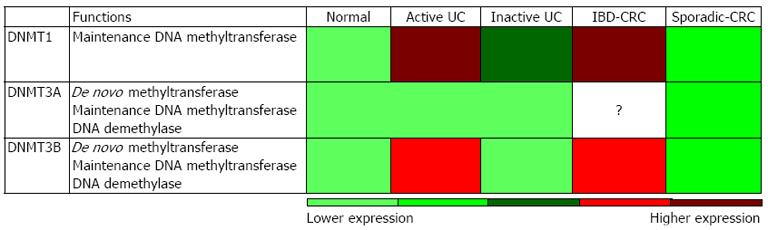
Figure 1 Potential relative expression levels of DNA methyltransferase in active-ulcerative colitis, inactive-ulcerative colitis, inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer and sporadic-colorectal cancer patient specimens consolidate from several studies.
DNA methyltransferase (DMNTs) is primarily responsible for DNA methylation maintenance, whereas DNMT3A/B have additional roles in de novo DNA methylation and demethylation functions. The relative DNMTs expressions were built on consolidated reports that were normalized to healthy controls to display potential relative expression in different inflammatory bowel disease associated diseases. UC: Ulcerative colitis; IBD-CRC: Inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer.
- Citation: Low D, Mizoguchi A, Mizoguchi E. DNA methylation in inflammatory bowel disease and beyond. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(32): 5238-5249
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i32/5238.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5238