Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4958-4965
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4958
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4958
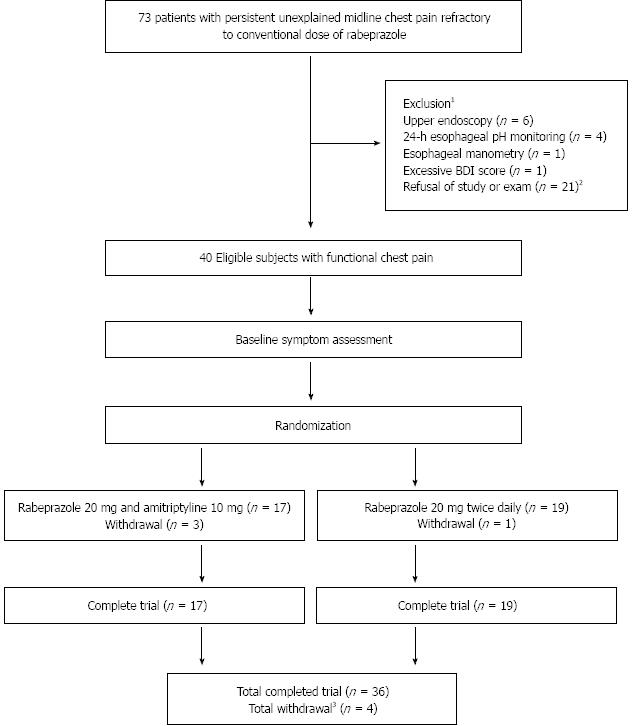
Figure 1 Flow of patients throughout the trial.
1Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy showed erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease (n = 5), and peptic ulcer disease (n = 1). Pathological acid exposure was found in four patients by ambulatory 24 h esophageal pH monitoring. An esophageal motility disorder was found in one patient by esophageal manometric examination. The Beck Depression Index score of one patient exceeded 19 points; 2Sixteen patients refused to take part in this study, and five patients refused examination by esophageal manometry or ambulatory 24 h esophageal pH monitoring; 3Out of 4 patients, three in group A withdrew because of an amitriptyline-associated adverse event. One patient in group B dropped out of the trial because of loss to follow-up. BDI: Beck Depression Inventory.
- Citation: Park SW, Lee H, Lee HJ, Park JC, Shin SK, Lee SK, Lee YC, Kim JE. Low-dose amitriptyline combined with proton pump inhibitor for functional chest pain. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4958-4965
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4958.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4958