Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4925-4934
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4925
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4925
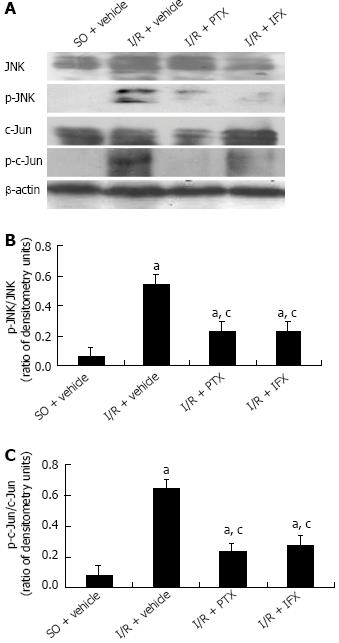
Figure 6 Tumor necrosis factor-α mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation response to mucosal injury in ischemia-reperfusion-induced intestine.
Equal quantities of protein were subjected to Western blotting analysis, and β-actin was used as the control for loading. The results were expressed as a ratio of densitometry units. A: Western blotting analysis; B: The ratio of p-c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and JNK; C: The ratio of p-c-Jun and c-Jun. Values are mean ± SE. Six rats were tested in each group. aP < 0.05 vs sham-operation(SO) rats pretreated with vehicle (SO + vehicle); cP < 0.05 vs ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) rats pretreated with vehicle (I/R + vehicle). PTX: Pentoxifylline; IFX: Infliximab.
- Citation: Yang Q, Zheng FP, Zhan YS, Tao J, Tan SW, Liu HL, Wu B. Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates JNK activation response to intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4925-4934
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4925.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4925