Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4897-4906
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4897
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4897
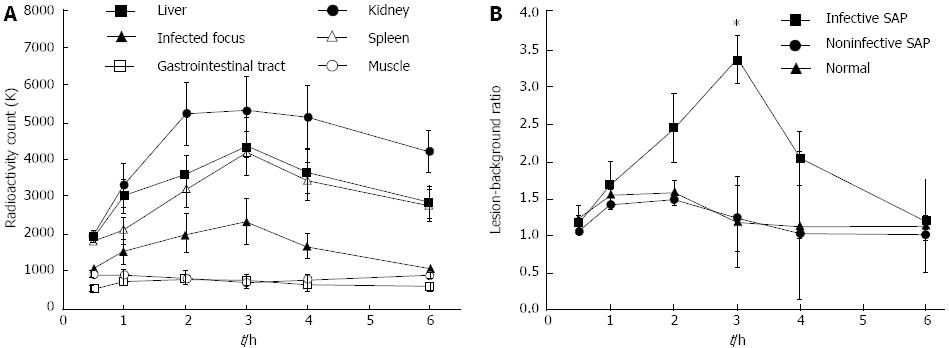
Figure 5 99mTc-ciprofloxacin scintigraphy results at different time points.
A: Curves showing radioactivity count changes over time in the abdominal tissues of swine with infected severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) are shown. These curves show high uptake in the kidneys and moderate uptake in the liver and spleen. No activity was observed in the areas of the muscle or gastrointestinal tract. The radioactive uptake by infectious foci increased gradually over time, reached a peak at 3 h, and then gradually decayed; B: Lesion-background ratio change curves for the normal pancreas, and non-infected and infected SAP pancreas in the swine model are shown. The curves show that the optimal lesion-background ratio occurred at 3 h after administration of Infecton in positive SAP animals.
- Citation: Wang JH, Sun GF, Zhang J, Shao CW, Zuo CJ, Hao J, Zheng JM, Feng XY. Infective severe acute pancreatitis: A comparison of 99mTc-ciprofloxacin scintigraphy and computed tomography. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4897-4906
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4897