Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4897-4906
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4897
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4897
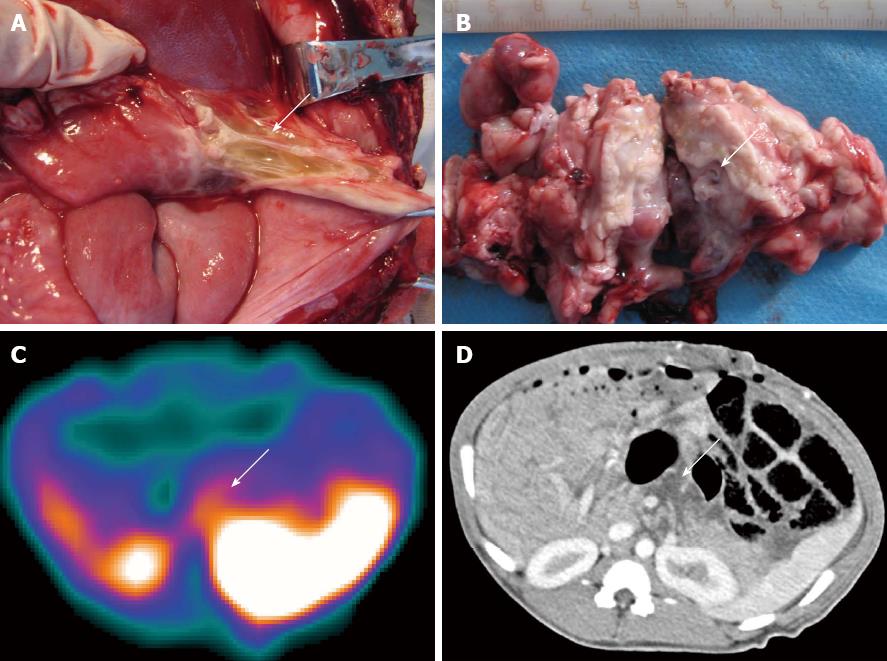
Figure 1 99mTc-ciprofloxacin scintigraphy has higher sensitivity and accuracy in the detection of bacterial infections than computed tomography (the swine came from group C).
A: The evidence of secondary infections in the peripancreatic fluid were confirmed by pathological examination and by bacterial smear or culture testing; B: Pancreatic necrosis was confirmed by pathological examination and by bacterial smear or culture testing; C: 99mTc-ciprofloxacin scintigraphy at 3 h demonstrated accumulation of radioactivity in the peripancreatic fluid and pancreatic necrosis (L/B = 3.37), indicating a true positive result; D: Enhanced computed tomography analysis showed low-density necrosis and peripancreatic fluid collection (arrow) without any indication of infection.
- Citation: Wang JH, Sun GF, Zhang J, Shao CW, Zuo CJ, Hao J, Zheng JM, Feng XY. Infective severe acute pancreatitis: A comparison of 99mTc-ciprofloxacin scintigraphy and computed tomography. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4897-4906
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4897.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4897