Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2013; 19(30): 4867-4876
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4867
Published online Aug 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4867
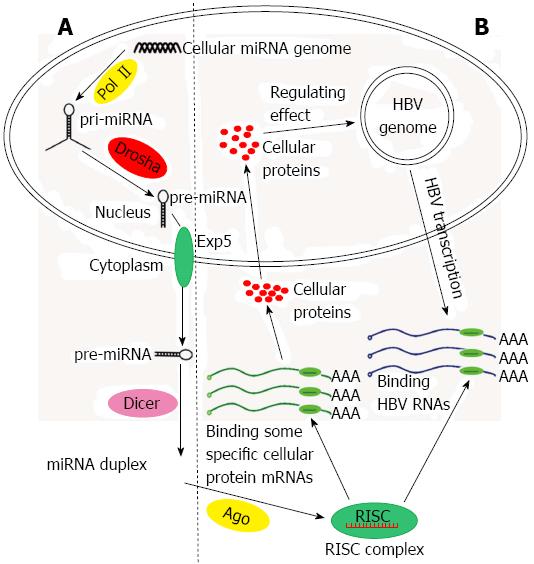
Figure 2 The biogenesis of human cellular microRNAs and the mechanism of the alteration hepatitis B virus gene transcription and replication.
For simplicity, not all participators are shown. A: The biogenesis of microRNAs (miRNAs); B: The mechanism of cellular miRNAs regulates hepatitis B virus (HBV) gene transcription and replication can be direct and indirect. Cellular miRNAs can target to HBV transcripts (HBV surface antigen mRNA, HBV x mRNA, DNA polymerase mRNA, etc.), causing the alteration of HBV expression. Cellular miRNAs can also target to the mRNAs of a number of key regulatory proteins (liver-enriched transcription factors, nuclear receptors, heme-oxygenase-1, DNA methyltransferases, etc.) in the process of HBV transcription and replication. Consequently, the amount of these proteins was changed, and the HBV gene transcription and replication were altered. RISC: RNA-induced silencing complex. Pol: Polymerase.
- Citation: Wei YF, Cui GY, Ye P, Chen JN, Diao HY. MicroRNAs may solve the mystery of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(30): 4867-4876
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i30/4867.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i30.4867