Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2013; 19(29): 4702-4717
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4702
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4702
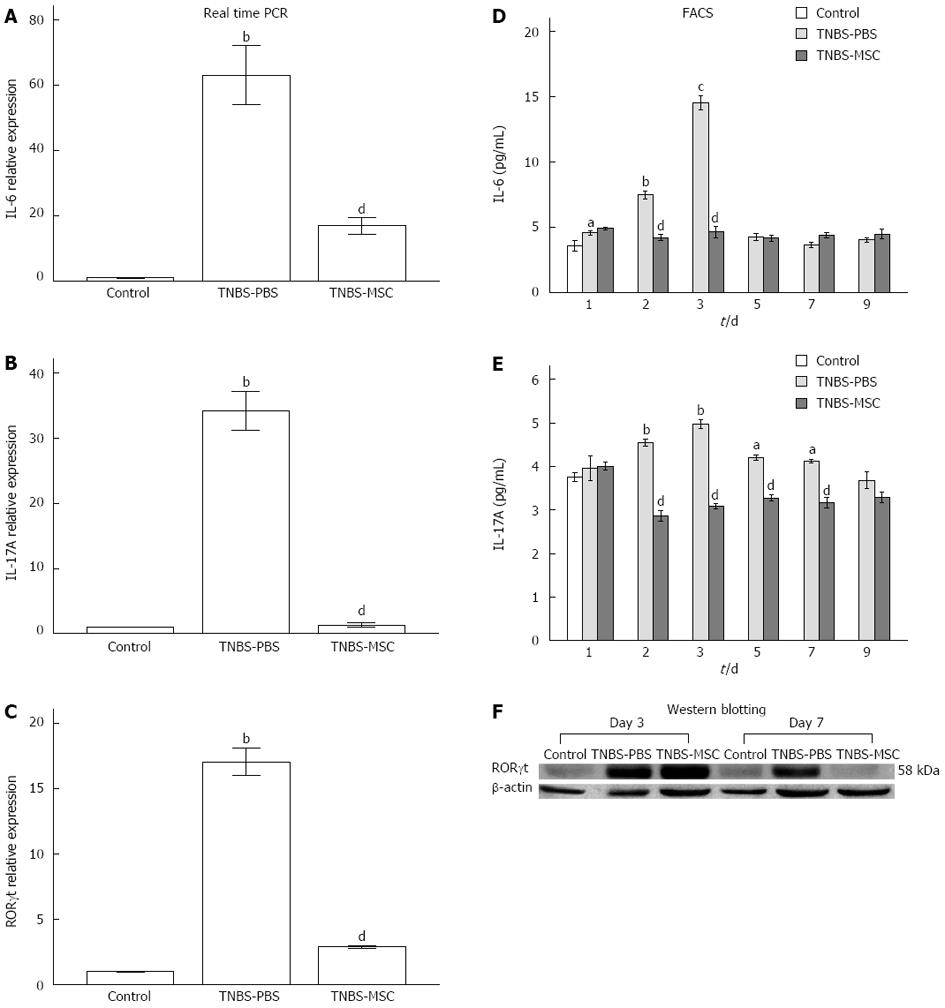
Figure 8 Changes in mRNA expression and colonic protein levels of Th17-related inflammatory mediators following treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.
A-C: Real-time polymerase chain reaction. The results showed a significant increase in mRNA expressions of interleukin (IL)-6, IL-17A and retinoid related orphan receptor gamma(t) (RORγt) when compared to controls (P < 0.01). After treatment with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, the levels of the above cytokines were reduced (P < 0.01); D, E: Flow cytometry. The same changes in colonic protein levels of IL-6 and IL-17A were further confirmed; F: Western blotting. The same changes in colonic protein levels of RORγt were further confirmed. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control; cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs TNBS-PBS. TNBS-MSC: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-mesenchymal stem cells; TNBS-PBS: Trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-phosphate-buffered saline.
- Citation: Chen QQ, Yan L, Wang CZ, Wang WH, Shi H, Su BB, Zeng QH, Du HT, Wan J. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate TNBS-induced colitis by modulating inflammatory and autoimmune responses. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(29): 4702-4717
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i29/4702.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4702