Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2013; 19(29): 4689-4701
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4689
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4689
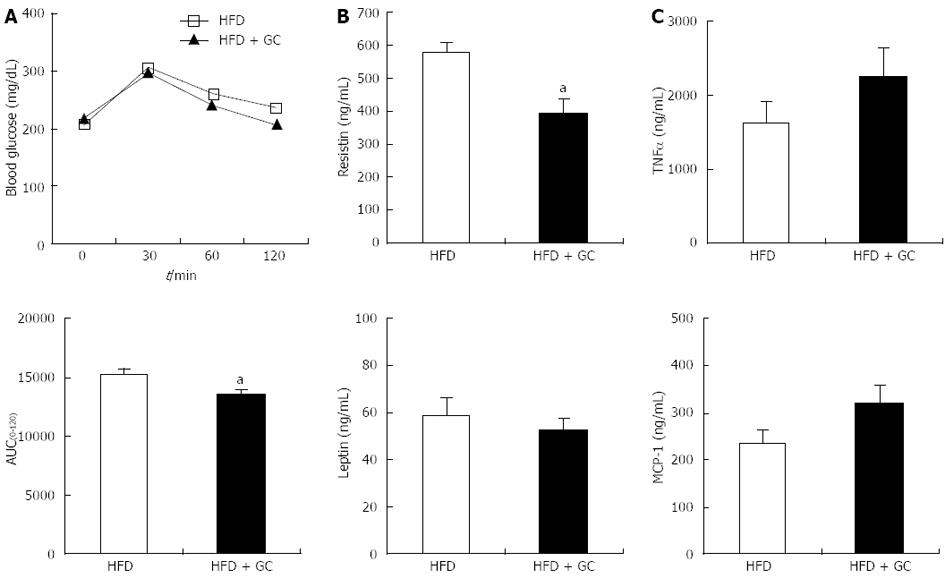
Figure 3 Effects of Garcinia Cambogia supplementation on glucose tolerance and plasma adipocytokine levels in mice fed a high-fat diet for 16 wk.
Data are expressed as the mean ± SE (n = 10). A: The intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test was performed on the 15th week of Garcinia Cambogia (GC) supplementation in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice. Following a 12-h fast, the mice were injected intraperitoneally with glucose (0.5 g/kg body weight). Blood glucose was then measured via the tail vein at the indicated time [above: Blood glucose values; below: Areas under the curves (AUC)]; B, C: Plasma levels of leptin, resistin, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were assayed after 16 wk of GC supplementation in HFD-fed mice. HFD, mice fed a high-fat diet alone; HFD + GC, mice fed a high-fat diet containing GC (1%, w/w). aP < 0.05 vs control group.
-
Citation: Kim YJ, Choi MS, Park YB, Kim SR, Lee MK, Jung UJ.
Garcinia Cambogia attenuates diet-induced adiposity but exacerbates hepatic collagen accumulation and inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(29): 4689-4701 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i29/4689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4689