Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2013; 19(29): 4689-4701
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4689
Published online Aug 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4689
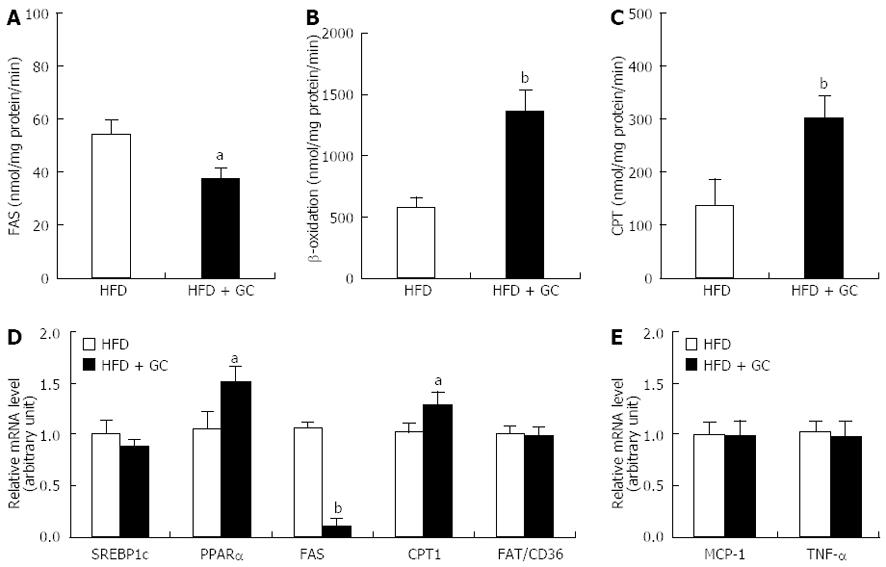
Figure 2 Effects of Garcinia Cambogia supplementation on fatty acid-regulating enzyme activity and gene expression in epididymal white adipose tissue of mice fed a high-fat diet for 16 wk.
Data are expressed as the mean ± SE (n = 10). A: Fatty acid synthase (FAS); B: β-oxidation; C: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT); D, E: Relative mRNA level. High-fat diet (HFD), mice fed a high-fat diet alone; HFD + Garcinia Cambogia (GC), mice fed a high-fat diet containing GC (1%, w/w). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control group. WAT: White adipose tissue; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α.
-
Citation: Kim YJ, Choi MS, Park YB, Kim SR, Lee MK, Jung UJ.
Garcinia Cambogia attenuates diet-induced adiposity but exacerbates hepatic collagen accumulation and inflammation. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(29): 4689-4701 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i29/4689.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i29.4689